A conserved and seemingly redundant Escherichia coli biotin biosynthesis gene expressed only during anaerobic growth
- PMID: 34597430
- PMCID: PMC8599648
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.14826
A conserved and seemingly redundant Escherichia coli biotin biosynthesis gene expressed only during anaerobic growth
Abstract
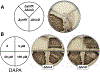
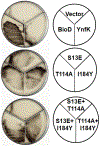
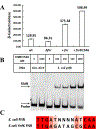
Biotin is an essential metabolic cofactor and de novo biotin biosynthetic pathways are widespread in microorganisms and plants. Biotin synthetic genes are generally found clustered into bio operons to facilitate tight regulation since biotin synthesis is a metabolically expensive process. Dethiobiotin synthetase (DTBS) catalyzes the penultimate step of biotin biosynthesis, the formation of 7,8-diaminononanoate (DAPA). In Escherichia coli, DTBS is encoded by the bio operon gene bioD. Several studies have reported transcriptional activation of ynfK a gene of unknown function, under anaerobic conditions. Alignments of YnfK with BioD have led to suggestions that YnfK has DTBS activity. We report that YnfK is a functional DTBS, although an enzyme of poor activity that is poorly expressed. Supplementation of growth medium with DAPA or substitution of BioD active site residues for the corresponding YnfK residues greatly improved the DTBS activity of YnfK. We confirmed that FNR activates transcriptional level of ynfK during anaerobic growth and identified the FNR binding site of ynfK. The ynfK gene is well conserved in γ-proteobacteria.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; anaerobic growth; biotin synthesis; dethiobiotin synthetase.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



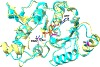
Similar articles
-
Substrate binding and carboxylation by dethiobiotin synthetase--a kinetic and X-ray study.Structure. 1995 Nov 15;3(11):1207-15. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00256-8. Structure. 1995. PMID: 8591031
-
Biochemical and structural characterization of the Arabidopsis bifunctional enzyme dethiobiotin synthetase-diaminopelargonic acid aminotransferase: evidence for substrate channeling in biotin synthesis.Plant Cell. 2012 Apr;24(4):1608-25. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.097675. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22547782 Free PMC article.
-
Dethiobiotin synthetase: the carbonylation of 7,8-diaminonanoic acid proceeds regiospecifically via the N7-carbamate.Biochemistry. 1995 Sep 5;34(35):10976-84. doi: 10.1021/bi00035a003. Biochemistry. 1995. PMID: 7669755
-
Oxygen regulated gene expression in Escherichia coli: control of anaerobic respiration by the FNR protein.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1991 Feb;59(2):65-76. doi: 10.1007/BF00445650. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1991. PMID: 1854188 Review.
-
FNR and its role in oxygen-regulated gene expression in Escherichia coli.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Aug;6(4):399-428. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04109.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990. PMID: 2248796 Review.
References
-
- Alexeev D, Baxter RL, Smekal O, and Sawyer L (1995) Substrate binding and carboxylation by dethiobiotin synthetase--a kinetic and X-ray study. Structure 3: 1207–1215. - PubMed
-
- Bhagavan HN, and Coursin DB (1967) Biotin content of blood in normal infants and adults. Am J Clin Nutr 20: 903–906. - PubMed
-
- Constantinidou C, Hobman JL, Griffiths L, Patel MD, Penn CW, Cole JA, and Overton TW (2006) A reassessment of the FNR regulon and transcriptomic analysis of the effects of nitrate, nitrite, NarXL, and NarQP as Escherichia coli K12 adapts from aerobic to anaerobic growth. J Biol Chem 281: 4802–4815. - PubMed
-
- Cronan JE (1988) Expression of the biotin biosynthetic operon of Escherichia coli is regulated by the rate of protein biotination. J Biol Chem 263: 10332–10336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

