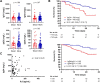
Serum IgG4 level predicts COVID-19 related mortality
- PMID: 34598853
- PMCID: PMC8461218
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2021.09.012
Serum IgG4 level predicts COVID-19 related mortality
Keywords: COVID-19; IgG4; SARS-CoV-2; immunoglobulins; subclasses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have not received any financial support or other benefits from commercial sources for the work reported in the manuscript, or any other financial interests that could create a potential conflict of interest or the appearance of a conflict of interest with regard to the work.
Figures
Comment in
-
Disguised aspects of IgG4.Eur J Intern Med. 2022 Jan;95:97. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2021.10.016. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Eur J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 34756504 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

