Cortical and subcortical brain structure in generalized anxiety disorder: findings from 28 research sites in the ENIGMA-Anxiety Working Group
- PMID: 34599145
- PMCID: PMC8486763
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-021-01622-1
Cortical and subcortical brain structure in generalized anxiety disorder: findings from 28 research sites in the ENIGMA-Anxiety Working Group
Abstract
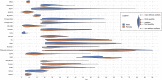
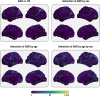
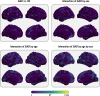
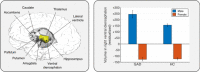
The goal of this study was to compare brain structure between individuals with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and healthy controls. Previous studies have generated inconsistent findings, possibly due to small sample sizes, or clinical/analytic heterogeneity. To address these concerns, we combined data from 28 research sites worldwide through the ENIGMA-Anxiety Working Group, using a single, pre-registered mega-analysis. Structural magnetic resonance imaging data from children and adults (5-90 years) were processed using FreeSurfer. The main analysis included the regional and vertex-wise cortical thickness, cortical surface area, and subcortical volume as dependent variables, and GAD, age, age-squared, sex, and their interactions as independent variables. Nuisance variables included IQ, years of education, medication use, comorbidities, and global brain measures. The main analysis (1020 individuals with GAD and 2999 healthy controls) included random slopes per site and random intercepts per scanner. A secondary analysis (1112 individuals with GAD and 3282 healthy controls) included fixed slopes and random intercepts per scanner with the same variables. The main analysis showed no effect of GAD on brain structure, nor interactions involving GAD, age, or sex. The secondary analysis showed increased volume in the right ventral diencephalon in male individuals with GAD compared to male healthy controls, whereas female individuals with GAD did not differ from female healthy controls. This mega-analysis combining worldwide data showed that differences in brain structure related to GAD are small, possibly reflecting heterogeneity or those structural alterations are not a major component of its pathophysiology.
© 2021. This is a U.S. government work and not under copyright protection in the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
PMP has received speakers honoraria from Daiichi Sankyo, Libbs, Sandoz, Novartis, and Abbot. NJ is MPI of a research-related grant from Biogen Inc, for work unrelated to this manuscript. JCS is consultant for PFIZER, SUNOVIAN, SANOFI, JOHNSON & JOHNSON, Livanova, and Boehringer Ingelheim. FA is Section Editor of NeuroImage: Clinical; has received speaker honoraria from Philips, Novartis, and Biogen Idec; and receives or has received research supports from the Italian Ministry of Health, AriSLA (Fondazione Italiana di Ricerca per la SLA), and the European Research Council. EC has received research support from the Italian Ministry of Health. MF is Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Neurology; received compensation for consulting services and/or speaking activities from Biogen Idec, Merck-Serono, Novartis, and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries; and receives research support from Biogen Idec, Merck-Serono, Novartis, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Roche, Italian Ministry of Health, Fondazione Italiana Sclerosi Multipla, and ARiSLA (Fondazione Italiana di Ricerca per la SLA). HJG has received travel grants and speakers honoraria from Fresenius Medical Care, Neuraxpharm, Servier, and Janssen Cilag as well as research funding from Fresenius Medical Care. GAF owns equity in Alto Neuroscience. MPP is an advisor to Spring Care, Inc., a behavioral health startup, he has received royalties for an article about methamphetamine in UpToDate. MBS has in the past 3 years been a consultant for Actelion, Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Aptinyx, Bionomics, BioXcel Therapeutics, Clexio, EmpowerPharm, Epivario, GW Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Roche/Genentech, and Oxeia Biopharmaceuticals; and has stock options in Oxeia Biopharmaceuticals and Epivario. PMT received partial grant support from Biogen, Inc., for research unrelated to this manuscript; consulted for Kairos Venture Capital, Inc., on projects unrelated to this manuscript. DJS has received research grants and/or consultancy honoraria from Lundbeck and Sun. Material support (for IOL site, led by MA and GJD) was provided by Neuronetics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Schmaal L, Hibar DP, Sämann PG, Hall GB, Baune BT, Jahanshad N, et al. Cortical abnormalities in adults and adolescents with major depression based on brain scans from 20 cohorts worldwide in the ENIGMA Major Depressive Disorder Working Group. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22:900–9. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.60. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boedhoe PSW, Schmaal L, Abe Y, Alonso P, Ameis SH, Anticevic A, et al. Cortical abnormalities associated with pediatric and adult obsessive-compulsive disorder: findings from the ENIGMA Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Working Group. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175:453–62. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.17050485. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH065413/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041120/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HD105002/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH100019/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH086686/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041156/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041025/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041106/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041117/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041148/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101497/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX000994/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- ZIA MH002798/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA041147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041093/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH109983/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH122389/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA041123/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041134/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH114023/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116147/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041022/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH117601/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K24 MH064122/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HD105002/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH014654/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041089/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH108509/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG058854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041028/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041048/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 MH117274/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH100259/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA MH002782/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041174/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101486/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

