Analyses of nicotine metabolism biomarker genetics stratified by sex in African and European Americans
- PMID: 34599228
- PMCID: PMC8486765
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-98883-z
Analyses of nicotine metabolism biomarker genetics stratified by sex in African and European Americans
Abstract
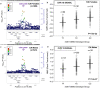
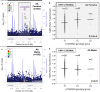
Nicotine is inactivated by the polymorphic CYP2A6 enzyme to cotinine and then to 3'hydroxycotinine. The Nicotine Metabolite Ratio (NMR; 3'hydroxycotinine/cotinine) is a heritable nicotine metabolism biomarker, varies with sex and ancestry, and influences smoking cessation and disease risk. We conducted sex-stratified genome-wide association studies of the NMR in European American (EA) and African American (AA) smokers (NCT01314001, NCT00666978). In EA females (n = 389) and males (n = 541), one significant (P < 5e-8) chromosome 19 locus was found (top variant: rs56113850, CYP2A6 (intronic), for C vs. T: females: beta = 0.67, P = 7.5e-22, 21.8% variation explained; males: beta = 0.75, P = 1.2e-37, 26.1% variation explained). In AA females (n = 503) and males (n = 352), the top variant was found on chromosome 19 but differed by sex (females: rs11878604, CYP2A6 (~ 16 kb 3'), for C vs. T: beta = - 0.71, P = 6.6e-26, 16.2% variation explained; males: rs3865454, CYP2A6 (~ 7 kb 3'), for G vs. T: beta = 0.64, P = 1.9e-19, 18.9% variation explained). In AA females, a significant region was found on chromosome 12 (top variant: rs12425845: P = 5.0e-9, TMEM132C (~ 1 Mb 5'), 6.1% variation explained) which was not significant in AA males. In AA males, significant regions were found on chromosomes 6 (top variant: rs9379805: P = 4.8e-9, SLC17A2 (~ 8 kb 5'), 8.0% variation explained) and 16 (top variant: rs77368288: P = 3.5e-8, ZNF469 (~ 92 kb 5'), 7.1% variation explained) which were not significant in AA females. Further investigation of these associations outside of chromosome 19 is required, as they did not replicate. Understanding how sex and ancestry influence nicotine metabolism genetics may improve personalized approaches for smoking cessation and risk prediction for tobacco-related diseases.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R. F. Tyndale has consulted for Quinn Emanuel and Ethismos. Dr. Benowitz has consulted with Achieve Life Sciences and Pfizer, companies that market or are developing smoking cessation medications, and has been a paid expert witness in litigation against tobacco companies. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Nakajima M, Yamamoto T, Nunoya K, Yokoi T, Nagashima K, Inoue K, et al. Characterization of CYP2A6 involved in 3′-hydroxylation of cotinine in human liver microsomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996;277(2):1010–1015. - PubMed
-
- Nakajima M, Yamamoto T, Nunoya K, Yokoi T, Nagashima K, Inoue K, et al. Role of human cytochrome P4502A6 in C-oxidation of nicotine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1996;24(11):1212–1217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

