Effectiveness of isolation measures with app support to contain COVID-19 epidemics: a parametric approach
- PMID: 34599662
- PMCID: PMC8486969
- DOI: 10.1007/s00285-021-01660-9
Effectiveness of isolation measures with app support to contain COVID-19 epidemics: a parametric approach
Abstract
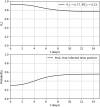
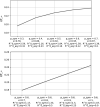
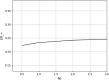
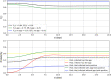
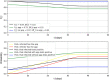
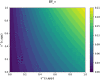
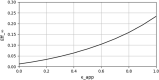
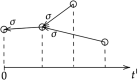
In this study, we analyze the effectiveness of measures aimed at finding and isolating infected individuals to contain epidemics like COVID-19, as the suppression induced over the effective reproduction number. We develop a mathematical model to compute the relative suppression of the effective reproduction number of an epidemic that such measures produce. This outcome is expressed as a function of a small set of parameters that describe the main features of the epidemic and summarize the effectiveness of the isolation measures. In particular, we focus on the impact when a fraction of the population uses a mobile application for epidemic control. Finally, we apply the model to COVID-19, providing several computations as examples, and a link to a public repository to run custom calculations. These computations display in a quantitative manner the importance of recognizing infected individuals from symptoms and contact-tracing information, and isolating them as early as possible. The computations also assess the impact of each variable on the mitigation of the epidemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Contact tracing; Epidemic models.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by the authors’ employer, Bending Spoons S.p.A, which was involved in the development of the contact tracing app adopted by the Italian Government.
Figures


Comment on
-
Quantifying SARS-CoV-2 transmission suggests epidemic control with digital contact tracing.Science. 2020 May 8;368(6491):eabb6936. doi: 10.1126/science.abb6936. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Science. 2020. PMID: 32234805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bendavid E, Mulaney B, Sood N, Shah S, Bromley-Dulfano R, Lai C, Weissberg Z, Saavedra-Walker R, Tedrow J, Bogan A, Kupiec T, Eichner D, Gupta R, Ioannidis JPA, Bhattacharya J (2021) COVID-19 antibody seroprevalence in Santa Clara County, California. Int J Epidemiol. 10.1093/ije/dyab010 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

