Effects of sevelamer carbonate versus calcium acetate on vascular calcification, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 34599865
- PMCID: PMC8841464
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13151
Effects of sevelamer carbonate versus calcium acetate on vascular calcification, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
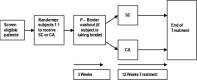
Hyperphosphatemia is present in most patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and has been associated with increased cardiovascular mortality. Phosphate binders (calcium-based and calcium free) are the mainstay pharmacologic treatment to lower phosphorus levels in patients with ESRD. We evaluated biochemical markers of vascular calcification, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) treated with sevelamer carbonate (SC) versus calcium acetate (CA). Fifty patients with CKD (stages 3 and 4) were enrolled and assigned to treatment with SC and CA for 12 weeks. At the end of the study the biomarkers of vascular calcification, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction were analyzed. A significant increase in HDL-cholesterol was observed with SC but not with CA in patients with CKD. Treatment with SC reduced serum phosphate, calcium phosphate, and FGF-23 levels and there was no change with CA treatment. The inflammatory markers IL-8, IFN-γ, and TNFα decreased with response to both treatments. The levels of IL-6 significantly increased with CA treatment and no change was observed in the SC treatment group. SC showed favorable effects on anti-inflammatory and vascular calcification biomarkers compared to CA treatment in patients with CKD stages 3 and 4 with normal phosphorous values.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01277497.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures



References
-
- Ketteler M, Block GA, Evenepoel P, et al. Diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease–mineral and bone disorder: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2017 clinical practice guideline update. Amm Intern Med. 2018;168:422‐430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

