Intra-population differences of apolipoproteins in the aqueous humor
- PMID: 34602085
- PMCID: PMC8487476
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-021-01555-0
Intra-population differences of apolipoproteins in the aqueous humor
Abstract
Background: Evidence suggests that proteins related to lipid metabolism, such as apolipoproteins, play an important role in the maintenance of normal vision. While several members of the apolipoprotein family are abundant in human aqueous humor (AH), their study remains difficult due to the AH's small volume, low protein concentration, and the invasive nature of sample collection. In this study, we report the use of Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to discover associations between AH apolipoproteins and race, gender, and ocular structure in patients with and without primary open angle glaucoma (POAG).
Methods: AH samples were collected from 231 patients undergoing phacoemulsification or glaucoma incisional surgery at the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University and subsequently analyzed via LC-MS/MS. The number of peptide spectrum matches (PSMs) for each protein was used as a semi-quantitative measure of relative protein levels. Parameters related to ocular structure were determined using Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Heidelberg Retinal Tomography (HRT). These data sets were probed for relationships between apolipoprotein levels and POAG, demographics (gender and race), and ocular structure.
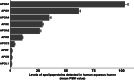
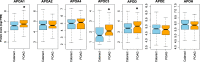
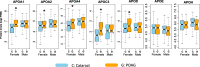
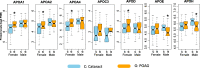
Results: A total of ten apolipoproteins were detected in the 231 collected AH samples, with six detected in 100% of the samples, one detected in almost 57% of the samples and three detected in less than 10% of the samples. The levels of APOA1, APOC3, and APOD were higher among POAG subjects. Stratification by gender and race revealed demographic-specific variations. The levels of five apolipoproteins (APOA1, APOA2, APOA4, APOC3, and APOD) were higher in female POAG patients, whereas no apolipoprotein levels were altered in male POAG patients. The levels of APOA1, APOA2, APOA4, and APOD were increased in glaucomatous African American patients, whereas APOE and APOH levels were decreased in glaucomatous Caucasian patients. We also found distinct associations between apolipoprotein levels and OCT and HRT parameters in patients with and without POAG.
Conclusions: The intra-population variation in apolipoprotein levels highlights the heterogeneity of glaucoma as a disease, suggesting the importance of personalized treatments. Gender and race-specific alterations may be associated with higher risks of POAG in females and members of the African American population.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of the aqueous humor proteome of primary angle closure and primary open angle glaucomas and age-related cataract eyes.Int Ophthalmol. 2019 Jan;39(1):69-104. doi: 10.1007/s10792-017-0791-0. Epub 2018 Jan 13. Int Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 29332228
-
Unveiling the levels and significance of different serpin family proteins in aqueous humor dynamics.BMC Ophthalmol. 2025 May 19;25(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12886-025-04119-3. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40389884 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Alterations in Aqueous Humor From Patients With Primary Open Angle Glaucoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 May 1;59(6):2635-2643. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-23434. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29847670 Free PMC article.
-
The aqueous humor proteome of primary open angle glaucoma: An extensive review.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Aug;197:108077. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108077. Epub 2020 May 27. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32470343 Review.
-
Advances in aqueous humor proteomics for biomarker discovery and disease mechanisms exploration: a spotlight on primary open angle glaucoma.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Apr 24;17:1397461. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1397461. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38721264 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum lipid and lipoprotein profiles and their association with intraocular pressure in primary open-angle glaucoma: an observational cross-sectional study in the Chinese population.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Sep 30;23(1):323. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02316-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39350087 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics of Aqueous Humor as a Source of Disease Biomarkers in Retinoblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 3;23(21):13458. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113458. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362243 Free PMC article.
-
AHP DB: a reference database of proteins in the human aqueous humor.Database (Oxford). 2024 Jan 29;2024:baae001. doi: 10.1093/database/baae001. Database (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 38284936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grus FH, Joachim SC, Pfeiffer N. Proteomics in ocular fluids. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2007;1:876–888. - PubMed
-
- Murthy KR, Rajagopalan P, Pinto SM, Advani J, Murthy PR, Goel R, Subbannayya Y, Balakrishnan L, Dash M, Anil AK, et al. Proteomics of human aqueous humor. OMICS. 2015;19:283–293. - PubMed
-
- Dominiczak MH, Caslake MJ. Apolipoproteins: metabolic role and clinical biochemistry applications. Ann Clin Biochem. 2011;48:498–515. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

