Key Factor Regulating Inflammatory Microenvironment, Metastasis, and Resistance in Breast Cancer: Interleukin-1 Signaling
- PMID: 34602858
- PMCID: PMC8486558
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/7785890
Key Factor Regulating Inflammatory Microenvironment, Metastasis, and Resistance in Breast Cancer: Interleukin-1 Signaling
Abstract
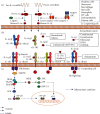
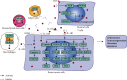
Breast cancer is one of the top-ranked cancers for incidence and mortality worldwide. The biggest challenges in breast cancer treatment are metastasis and drug resistance, for which work on molecular evaluation, mechanism studies, and screening of therapeutic targets is ongoing. Factors that lead to inflammatory infiltration and immune system suppression in the tumor microenvironment are potential therapeutic targets. Interleukin-1 is known as a proinflammatory and immunostimulatory cytokine, which plays important roles in inflammatory diseases. Recent studies have shown that interleukin-1 cytokines drive the formation and maintenance of an inflammatory/immunosuppressive microenvironment through complex intercellular signal crosstalk and tight intracellular signal transduction, which were found to be potentially involved in the mechanism of metastasis and drug resistance of breast cancer. Some preclinical and clinical treatments or interventions to block the interleukin-1/interleukin-1 receptor system and its up- and downstream signaling cascades have also been proven effective. This study provides an overview of IL-1-mediated signal communication in breast cancer and discusses the potential of IL-1 as a therapeutic target especially for metastatic breast cancer and combination therapy and current problems, aiming at enlightening new ideas in the study of inflammatory cytokines and immune networks in the tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2021 Fengjie Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IL20RA signaling enhances stemness and promotes the formation of an immunosuppressive microenvironment in breast cancer.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(6):2564-2580. doi: 10.7150/thno.45280. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33456560 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine-mediated therapeutic resistance in breast cancer.Cytokine. 2018 Aug;108:151-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.03.020. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 29609137 Review.
-
Interleukin-1 signaling in solid organ malignancies.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022 Jan;1877(1):188670. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188670. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34923027 Review.
-
The significant role of interleukin-6 and its signaling pathway in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Dec;108:1415-1424. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.177. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30372844 Review.
-
Adipokines as therapeutic targets in breast cancer treatment.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Nov;22(11):941-953. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1538356. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 30332900 Review.
Cited by
-
Study on the mechanism of MDSC-platelets and their role in the breast cancer microenvironment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 9;12:1310442. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1310442. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38404689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of tumor-associated macrophages on the pyroptosis of breast cancer tumor cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Aug 4;21(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01208-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37542283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein‑Barr virus as a promoter of tumorigenesis in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Aug;52(2):72. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5275. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37417334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Interaction between Carvacrol and Thymol, Major Compounds of Ptychotis verticillata Essential Oil: Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Activities against Breast Cancer Lines.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 20;14(8):1037. doi: 10.3390/life14081037. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202779 Free PMC article.
-
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) signaling pathways and cancer: foes versus allies.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Oct 27;23(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03080-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37891636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

