"Unimportant" Molecules?-Part 1
Abstract
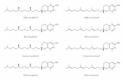
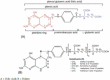
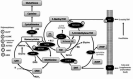
About a century ago when research into the nutritional components of food began, scientists were limited by the technology and physiological understanding of the time. Nonetheless, this pioneering research revealed the importance of many nutrients for the maintenance of life and prevention of overt deficiency diseases. Unfortunately, the necessary simplifications led to the unrecognized assumption that the constituents in food not required for life were not important. This justified growing food chemically rather than organically because essential nutrients were largely (but not entirely) conserved. However, as technology advanced-especially at the turn of this century-much was revealed. Nutrients considered single molecules when discovered were now realized to represent multiple variants and vitamers with significantly different physiological effects, and many of the molecules considered "unimportant" have huge impacts on health and resistance to disease.
Copyright © 2021 InnoVision Professional Media Inc.
Figures
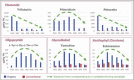
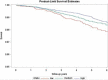
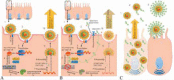
Similar articles
-
"Unimportant" Molecules?-Part 2.Integr Med (Encinitas). 2023 Jul;22(3):6-9. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2023. PMID: 37534021 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and nutritional assessment of GM plants and derived food and feed: the role of animal feeding trials.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Mar;46 Suppl 1:S2-70. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.02.008. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18328408 Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory drugs in the 21st century.Subcell Biochem. 2007;42:3-27. doi: 10.1007/1-4020-5688-5_1. Subcell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17612044 Review.
-
AN EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BACTERIAL ALLERGY.J Exp Med. 1926 Nov 30;44(6):753-76. doi: 10.1084/jem.44.6.753. J Exp Med. 1926. PMID: 19869221 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
Cited by
-
"Unimportant" Molecules?-Part 2.Integr Med (Encinitas). 2023 Jul;22(3):6-9. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2023. PMID: 37534021 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Vitamers.Integr Med (Encinitas). 2025 Jun;24(3):6-8. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2025. PMID: 40453232 Free PMC article.
-
Health Medicine.Integr Med (Encinitas). 2022 Dec;21(6):8-14. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2022. PMID: 36820267 Free PMC article.
-
Open Letter to President Trump. How to Cure the Disease Treatment System? Make It a Health Care System.Integr Med (Encinitas). 2024 Dec;23(6):6-8. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2024. PMID: 39830430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Semba RD. The discovery of the vitamins. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2012;82(5):310-315. doi:10.1024/0300-9831/a00012. - PubMed
-
- Vitamin.Wikipedia. Updated August 21, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin.
-
- Hounsome N, Hounsome B, Tomos D, Edwards-Jones G. Plant metabolites and nutritional quality of vegetables. J Food Sci. 2008;73(4):R48-R65. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00716.. - PubMed
-
- Beyond α-tocopherol: a review of natural vitamin E’s therapeutic potential in human health and disease: Part I | Longevity Medicine Review (Imreview.com). Accessed August 2, 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
