A Systematic Approach to Pregnancy-Specific Liver Disorders
- PMID: 34602893
- PMCID: PMC8475247
A Systematic Approach to Pregnancy-Specific Liver Disorders
Abstract
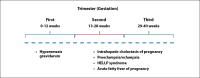
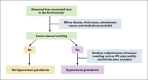
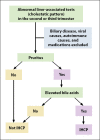
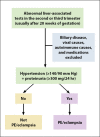
Consultation for liver disease during pregnancy is challenging for both the hepatologist and gynecologist, as normal physiologic changes during pregnancy can mimic chronic liver disease. Pregnancy-specific liver disorders are leading causes of abnormal liver function tests during pregnancy. Moreover, up to 3% of all pregnant women in developed countries experience liver diseases nonspecific to pregnancy. When severe, pregnancy-specific liver disorders are associated with significant morbidity and mortality for both the mother and the fetus. The main factors that determine maternal prognosis are the type of liver disease; degree of impaired synthetic, metabolic, and excretory liver function; and timing of delivery. This article focuses on a systematic approach to diagnosing and managing pregnancy-specific liver disorders, which includes understanding normal findings in pregnancy, excluding liver diseases nonspecific to pregnancy, factoring in trimester status, and using clinical clues to make a diagnosis and provide treatment in a timely fashion.
Keywords: Liver disease; acute fatty liver of pregnancy; eclampsia; hyperemesis gravidarum; intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy; preeclampsia; pregnancy.
Copyright © 2021, Gastro-Hep Communications, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liver diseases unique to pregnancy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2008;44(5):337-45. Medicina (Kaunas). 2008. PMID: 18541949 Review.
-
Liver disease in pregnancy.Med Clin North Am. 1996 Sep;80(5):1167-87. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(05)70484-3. Med Clin North Am. 1996. PMID: 8804379 Review.
-
Liver diseases in pregnancy: diseases unique to pregnancy.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Nov 21;19(43):7639-46. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7639. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24282353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver disease in pregnancy.Hepatology. 2008 Mar;47(3):1067-76. doi: 10.1002/hep.22130. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18265410 Review.
-
Advances in understanding and treating liver diseases during pregnancy: A review.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 7;21(17):5183-90. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5183. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25954092 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the prevalence and associated factors of elevated liver enzymes and dyslipidemia during pregnancy.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 1;15(1):3967. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88798-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39893319 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term risk of chronic liver disease after pre-eclampsia.Int J Epidemiol. 2025 Apr 12;54(3):dyaf072. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyaf072. Int J Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 40489944 Free PMC article.
-
State of the Art in Hepatic Dysfunction in Pregnancy.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Oct 31;9(11):1481. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9111481. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828527 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Westbrook RH, Dusheiko G, Williamson C. Pregnancy and liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64(4):933–945. - PubMed
-
- Shekhar S, Diddi G. Liver disease in pregnancy. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;54(5):475–482. - PubMed
-
- Meah VL, Cockcroft JR, Backx K, Shave R, Stöhr EJ. Cardiac output and related haemodynamics during pregnancy: a series of meta-analyses. Heart. 2016;102(7):518–526. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
