Image Features of Magnetic Resonance Angiography under Deep Learning in Exploring the Effect of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Nursing on the Neurological Function Recovery of Patients with Acute Stroke
- PMID: 34602911
- PMCID: PMC8449730
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/1197728
Image Features of Magnetic Resonance Angiography under Deep Learning in Exploring the Effect of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Nursing on the Neurological Function Recovery of Patients with Acute Stroke
Abstract
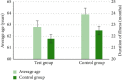
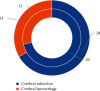
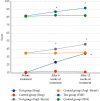
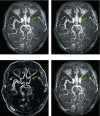
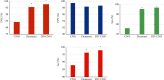
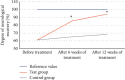
This study was to explore the effects of imaging characteristics of magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) based on deep learning on the comprehensive rehabilitation nursing on the neurological recovery of patients with acute stroke. In this study, 84 patients with acute stroke who were treated in hospital were selected as the research objects, and they were rolled into a control group (routine care) and an experimental group (comprehensive rehabilitation care). The dense dilated block-convolution neural network (DD-CNN) algorithm under deep learning for cerebrovascular was adopted to assess the effect of comprehensive rehabilitation care on the neurological recovery of patients with acute stroke. The results showed that the Berg scale scores, Fugl-Meyer scores, and Functional Independence Measure (FIM) scores of the experimental group of patients after 6 weeks and 12 weeks of comprehensive rehabilitation nursing were greatly different from those before treatment, showing statistical differences (P < 0.05). Compared with conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images, MRA images based on CNN algorithm, Dense Net algorithm, and DD-CNN algorithm can more clearly show the patient's cerebral artery occlusion. The average dice similarity coefficient (DSC) values of CNN algorithm, Dense Net algorithm, and DD-CNN algorithm were determined to be 84.3%, 95.7%, and 97.8%, respectively; the average sensitivity (Sen) values of the three algorithms were 76.1%, 95.4%, and 96.8%, respectively; and the average accuracy (Acc) values were 87.9%, 96.3%, and 97.9%, respectively. Thus, there were statistically obvious differences among the three algorithms in terms of average values of DSC, Sen, and Acc (P < 0.05). The MRA images processed by the DD-CNN algorithm showed that the degree of neurological recovery of the experimental group was observably greater than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically obvious (P < 0.05). In short, the image features of MRA based on the deep learning DD-CNN algorithm showed good application value in studying the effect of comprehensive rehabilitation nursing on the neurological recovery of patients with acute stroke, and it was worthy of promotion.
Copyright © 2021 Rui Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of intelligent convolutional neural network -based algorithms on head computed tomography evaluation and comprehensive rehabilitation acupuncture therapy for patients with cerebral infarction.J Neurosci Methods. 2024 Sep;409:110185. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2024.110185. Epub 2024 Jun 6. J Neurosci Methods. 2024. PMID: 38851543
-
Use of Head and Neck Magnetic Resonance Angiography to Explore Neurological Function Recovery and Impact of Rehabilitation Nursing on Patients with Acute Stroke.World Neurosurg. 2021 May;149:470-480. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.11.116. World Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33940698
-
Image Features of Magnetic Resonance Imaging under the Deep Learning Algorithm in the Diagnosis and Nursing of Malignant Tumors.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2021 Aug 30;2021:1104611. doi: 10.1155/2021/1104611. eCollection 2021. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34548850 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear medicine in the rehabilitative treatment evaluation in stroke recovery. Role of diaschisis resolution and cerebral reorganization.Eura Medicophys. 2007 Jun;43(2):221-39. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Eura Medicophys. 2007. PMID: 17268387 Review.
-
Application of Deep Learning to Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2022 Apr;43(2):147-152. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2022.02.004. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2022. PMID: 35339255 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Value of Image Features of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Intracranial Hemorrhage and Cerebral Infarction.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Jul 12;2022:6495568. doi: 10.1155/2022/6495568. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35935302 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
