Implant Replacement or Removal: What Happens after Capsular Contracture? A German Study Examining Breast Implant Revision Surgery and Patient Choices in 946 Cases
- PMID: 34602940
- PMCID: PMC8436706
- DOI: 10.1159/000509598
Implant Replacement or Removal: What Happens after Capsular Contracture? A German Study Examining Breast Implant Revision Surgery and Patient Choices in 946 Cases
Abstract
Introduction: Capsular contracture most often leads to implant revision surgery for aesthetic or reconstructive purposes. However, little is known about which operation is chosen when revision surgery has to be performed. We performed analysis of revision indications and performed revision surgery considering implant removal or replacement and additional surgical procedures. To our knowledge, this study presents the largest German single-center analysis regarding implant revision surgery after the onset of complications.
Methods: Retrospective 10-year data analysis of a single-center population undergoing breast implant revision surgery.
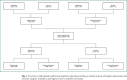
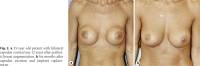
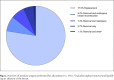
Results: Capsular contracture was the most frequent finding before reoperation, both removal and replacement (p < 0.05). It was linked to longer duration of in situ implant placement (p < 0.05) and more frequently in reconstructive patients (p < 0.05). Implant replacement was performed more often before definite implant removal for reconstructive patients (p < 0.05). Mean duration of in situ implant placement before definite removal was lower for reconstructive patients (p = 0.005). Overall reconstructive patients were older than aesthetic patients (p < 0.05). After implant removal, 61.7% of aesthetic patients chose to undergo mastopexy, 54.7% of reconstructive patients opted for autologous breast reconstruction, and 25.4% did not choose an additional surgical procedure after implant removal.
Conclusion: Significant differences are observed for reconstructive and aesthetic patients regarding indication leading to revision surgery, time of revision surgery, and the type of performed revision surgery itself. After implant removal, more than 60% of aesthetic patients undergo mastopexy, more than half of reconstructive patients choose autologous breast reconstruction, and over a quarter of patients choose no additional surgical procedures.
Keywords: Breast augmentation; Breast surgery; Capsular contracture; Implants; Mastopexy.
Copyright © 2020 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Decreasing Time Intervals in Recurring Capsular Contracture? A Single Center Retrospective Study over 6 Years.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023 Mar 10;11(3):e4872. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004872. eCollection 2023 Mar. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023. PMID: 36910725 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of implant surface on the recurrence rates of capsular contracture following revision breast surgery: Early results from a single surgeon retrospective comparative study.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2021 Dec;74(12):3307-3315. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2021.05.016. Epub 2021 Jun 6. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2021. PMID: 34210625
-
The reoperation cascade after breast augmentation with implants: what the patient needs to know.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013 Mar;66(3):313-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2012.09.033. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013. PMID: 23102610
-
Risk factors for developing capsular contracture in women after breast implant surgery: A systematic review of the literature.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018 Sep;71(9):e29-e48. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2018.05.022. Epub 2018 Jun 9. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018. PMID: 29980456
-
Prosthetic breast reconstruction: indications and update.Gland Surg. 2016 Apr;5(2):174-86. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2015.07.01. Gland Surg. 2016. PMID: 27047785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drainless Implant Removal: A Technique to Minimize Breast Disfigurement After Explantation.Eplasty. 2024 Nov 15;24:QA24. eCollection 2024. Eplasty. 2024. PMID: 40529381 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
[Breast implant removal and simultaneous aesthetic optimization : Possibilities, technical considerations and outcome analysis].Chirurgie (Heidelb). 2024 Jan;95(1):63-70. doi: 10.1007/s00104-023-01972-0. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Chirurgie (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 37878065 German.
-
What Can We Learn from Breast Implant Explantation: a 28-Year, Multicenter Retrospective Study of 1004 Explantation Cases.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023 Oct;47(5):1743-1750. doi: 10.1007/s00266-023-03365-4. Epub 2023 May 18. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 37204467 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Salvage Auto-augmentation: Contemporary Strategy for Management of the Breast Explantation Patient.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023 Mar 6;11(3):e4860. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004860. eCollection 2023 Mar. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023. PMID: 36891568 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion to Autologous Breast Reconstruction with Latissimus Dorsi and Immediate Fat Grafting in Patients with Previous Implant Failure: An Efficient, Reproducible, and Safe Technique.Indian J Plast Surg. 2024 Feb 9;57(1):16-23. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1779479. eCollection 2024 Feb. Indian J Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38450013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kühn S, Rieger UM. Ästhetische Operationen - nimmt der Trend zu? gynäkologische praxis. 2018;((44/2)):309–316.
-
- International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery [Internet] ISAPS INTERNATIONAL SURVEY ON AESTHETIC/COSMETIC PROCEDURES performed in. 2018 Available from https://www.isaps.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/ISAPS-Global-Survey-Res....
-
- Champaneria MC, Wong WW, Hill ME, Gupta SC. The evolution of breast reconstruction: a historical perspective. World J Surg. 2012 Apr;36((4)):730–42. - PubMed
-
- Billner M, Wirthmann A, Reif S, Rieger UM. Poly Implant Prothèse and Rofil Substandard Breast Implant Explantations from a Large German Single Centre from 2011 to 2014: A Comparative Study. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2016 Aug;40((4)):507–13. - PubMed
-
- Gabriel SE, Woods JE, O'Fallon WM, Beard CM, Kurland LT, Melton LJ., 3rd Complications leading to surgery after breast implantation. N Engl J Med. 1997 Mar;336((10)):677–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

