The Role of the Carnitine/Organic Cation Transporter Novel 2 in the Clinical Outcome of Patients With Locally Advanced Esophageal Carcinoma Treated With Oxaliplatin
- PMID: 34603016
- PMCID: PMC8481660
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.684545
The Role of the Carnitine/Organic Cation Transporter Novel 2 in the Clinical Outcome of Patients With Locally Advanced Esophageal Carcinoma Treated With Oxaliplatin
Abstract
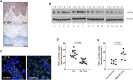
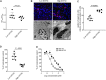
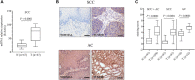
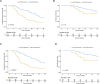
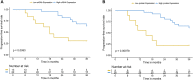
Esophageal cancer is the ninth most common malignancy worldwide, ranking sixth in mortality. Platinum-based chemotherapy is commonly used for treating locally advanced esophageal cancer, yet it is ineffective in a large portion of patients. There is a need for reliable molecular markers with direct clinical application for a prospective selection of patients who can benefit from chemotherapy and patients in whom toxicity is likely to outweigh the benefit. The cytotoxic activity of platinum derivatives largely depends on the uptake and accumulation into cells, primarily by organic cation transporters (OCTs). The aim of the study was to investigate the impact of OCT expression on the clinical outcome of patients with esophageal cancer treated with oxaliplatin. Twenty patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) were prospectively enrolled and surgical specimens used for screening OCT expression level by western blotting and/or immunostaining, and for culture of cancer cells. Sixty-seven patients with SCC who received oxaliplatin and for whom follow-up was available were retrospectively assessed for organic cation/carnitine transporter 2 (OCTN2) expression by real time RT-PCR and immunostaining. OCTN2 staining was also performed in 22 esophageal adenocarcinomas. OCTN2 function in patient-derived cancer cells was evaluated by assessing L-carnitine uptake and sensitivity to oxaliplatin. The impact of OCTN2 on oxaliplatin activity was also assessed in HEK293 cells overexpressing OCTN2. OCTN2 expression was higher in tumor than in normal tissues. In patient-derived cancer cells and HEK293 cells, the expression of OCTN2 sensitized to oxaliplatin. Patients treated with oxaliplatin who had high OCTN2 level in the tumor tissue had a reduced risk of recurrence and a longer survival time than those with low expression of OCTN2 in tumor tissue. In conclusion, OCTN2 is expressed in esophageal cancer and it is likely to contribute to the accumulation and cytotoxic activity of oxaliplatin in patients with esophageal carcinoma treated with oxaliplatin.
Keywords: OCTN2; biomarker; carnitine transporter; esophageal cancer; oxaliplatin.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Chen, Gai, Zhang, Yang, Hu, Chen, Yang, Hörmann, Kullak-Ublick and Visentin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxaliplatin transport mediated by organic cation/carnitine transporters OCTN1 and OCTN2 in overexpressing human embryonic kidney 293 cells and rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Aug;338(2):537-47. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.181297. Epub 2011 May 23. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21606177
-
Luteolin potentiates the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cell lines to oxaliplatin through the PPARγ/OCTN2 pathway.Anticancer Drugs. 2014 Oct;25(9):1016-27. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000125. Anticancer Drugs. 2014. PMID: 25075794
-
Expression and localization of carnitine/organic cation transporter OCTN1 and OCTN2 in ocular epithelium.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Nov;49(11):4844-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-1528. Epub 2008 Jul 18. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18641280
-
Recent advances in drug delivery via the organic cation/carnitine transporter 2 (OCTN2/SLC22A5).Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Aug;22(8):715-726. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1502273. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 30016594 Review.
-
Pharmacological and pathophysiological roles of carnitine/organic cation transporters (OCTNs: SLC22A4, SLC22A5 and Slc22a21).Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2013 Jan;34(1):29-44. doi: 10.1002/bdd.1816. Epub 2012 Oct 14. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2013. PMID: 22952014 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomic profiling of triple negative breast cancer cells suggests that valproic acid can enhance the anticancer effect of cisplatin.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 5;10:1014798. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1014798. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36544904 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Organic Cation Transporters in the Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Drug-Drug Interactions of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2101. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032101. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Strategies for Aberrant Lipid Metabolism Reprogramming and the Immune Microenvironment in Esophageal Cancer: A Review.J Oncol. 2022 Sep 5;2022:4257359. doi: 10.1155/2022/4257359. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36106333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cooper J. S., Guo M. D., Herskovic A., Macdonald J. S., Martenson J. A., Jr., Al-Sarraf M., et al. (1999). Chemoradiotherapy of Locally Advanced Esophageal Cancer: Long-Term Follow-Up of a Prospective Randomized Trial (RTOG 85-01). Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. JAMA 281, 1623–1627. 10.1001/jama.281.17.1623 - DOI - PubMed
-
- D'argenio G., Petillo O., Margarucci S., Torpedine A., Calarco A., Koverech A., et al. (2010). Colon OCTN2 Gene Expression Is Up-Regulated by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma in Humans and Mice and Contributes to Local and Systemic Carnitine Homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 27078–27087. 10.1074/jbc.M110.109678 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

