Mitragynine (Kratom)-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Mice Resemble Δ9-THC and Morphine Effects: Reversal by Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Antagonism
- PMID: 34603022
- PMCID: PMC8481666
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.708055
Mitragynine (Kratom)-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Mice Resemble Δ9-THC and Morphine Effects: Reversal by Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Antagonism
Abstract
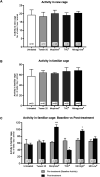
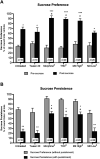
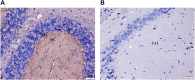
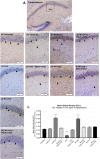
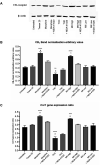
Kratom is a widely abused plant-based drug preparation with a global interest in recent years, well beyond its native grounds in Southeast Asia. Mitragynine, its major psychoactive constituent is known to exhibit opioid-like behavioral effects with resultant neuroplasticity in the brain reward system. Its chronic administration is associated with cognitive impairments in animal studies. However, the underlying molecular mechanism for such a deficit remains elusive. In this study, the involvement of cannabinoid type-1 (CB1) receptors in cognitive deficits after chronic mitragynine exposures was investigated for 28 days (with incremental dose sensitization from 1 to 25 mg/kg) in adult male Swiss albino mice using the IntelliCage® system. Chronic high-dose mitragynine exposure (5-25 mg/kg, intraperitoneal [i.p.]), but not low-dose exposure (1-4 mg/kg, i.p.), induced hyperlocomotion, potentiated the preference for sucrose reward, increased resistance to punishment, and impaired place learning and its reversal. Comparable deficits were also observed after chronic treatments with Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC, 2 mg/kg, i.p.) or morphine (5 mg/kg, subcutaneous). Mitragynine-, morphine-, and THC-induced learning and memory deficits were reversed by co-treatment with the CB1 receptor antagonist, NIDA-41020 (10 mg/kg, i.p.). A significant upregulation of CB1 receptor expression was found in the hippocampal CA1 region and ventral tegmental area after chronic high-dose mitragynine and morphine, whereas a downregulation was observed after chronic THC. In conclusion, the present study suggests a plausible role of the CB1 receptor in mediating the dose-dependent cognitive deficits after chronic high-dose mitragynine exposure. This also highlights the potential of CB1 receptor antagonism in ameliorating the cognitive deficits associated with long-term kratom/mitragynine consumption in humans.
Keywords: cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1); cognition; kratom; mitragynine; morphine; Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Copyright © 2021 Iman, Ahmad, Mohd Yusof, Talib, Norazit, Kumar, Mehat, Hassan, Müller and Muzaimi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chronic mitragynine (kratom) enhances punishment resistance in natural reward seeking and impairs place learning in mice.Addict Biol. 2017 Jul;22(4):967-976. doi: 10.1111/adb.12385. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Addict Biol. 2017. PMID: 26990882
-
Mitragynine (Kratom)-Withdrawal behaviour and cognitive impairments can be ameliorated by an epigenetic mechanism.Br J Pharmacol. 2024 Jul;181(13):2070-2084. doi: 10.1111/bph.16352. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Br J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38523471
-
Abuse potential and adverse cognitive effects of mitragynine (kratom).Addict Biol. 2016 Jan;21(1):98-110. doi: 10.1111/adb.12185. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Addict Biol. 2016. PMID: 25262913
-
Behavioral effects of cannabinoid agents in animals.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1999;13(3):243-81. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v13.i3.20. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10803637 Review.
-
New perspectives in the studies on endocannabinoid and cannabis: abnormal behaviors associate with CB1 cannabinoid receptor and development of therapeutic application.J Pharmacol Sci. 2004 Dec;96(4):362-6. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fmj04003x2. Epub 2004 Dec 10. J Pharmacol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15599103 Review.
Cited by
-
Goofballing of Opioid and Methamphetamine: The Science Behind the Deadly Cocktail.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 7;13:859563. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.859563. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35462918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoid mechanisms contribute to the therapeutic efficacy of the kratom alkaloid mitragynine against neuropathic, but not inflammatory pain.Life Sci. 2023 Sep 1;328:121878. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121878. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37392779 Free PMC article.
-
IntelliCage: the development and perspectives of a mouse- and user-friendly automated behavioral test system.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Jan 3;17:1270538. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1270538. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38235003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adolescent kratom exposure affects cognitive behaviours and brain metabolite profiles in Sprague-Dawley rats.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 28;13:1057423. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1057423. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36518677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Zaher A. O., Mostafa M. G., Farghaly H. S., Hamdy M. M., Abdel-Hady R. H. (2013). Role of Oxidative Stress and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Morphine-Induced Tolerance and Dependence in Mice. Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid. Behav. Brain Res. 247, 17–26. 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.02.034 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allen Institute for Brain Science (2004). Allen Brain Atlas: Mouse Brain©. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

