Intervention of Gastrodin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Mechanism
- PMID: 34603025
- PMCID: PMC8481818
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.710722
Intervention of Gastrodin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Mechanism
Abstract
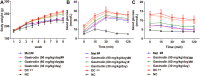
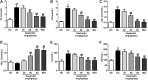
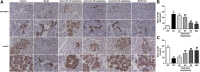
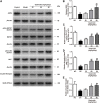
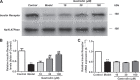
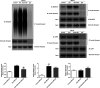
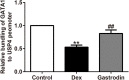
As a severe metabolic disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has become a serious threat to human health in recent years. Gastrodin, as a primary chemical constituent in Gastrodia elata Blume, has antidiabetic effects. However, the possible mechanisms are unclear. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects and possible mechanisms of gastrodin on the treatment of T2DM. In vivo, after treatment with gastrodin for 6 weeks, fasting blood glucose levels, blood lipid metabolism, and insulin sensitivity index values were remarkably reduced compared with those of the diabetic control group. The values of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase also showed that gastrodin alleviates liver toxicity caused by diabetes. Moreover, gastrodin relieved pathological damage to the pancreas in T2DM rats. In vitro, gastrodin alleviated insulin resistance by increasing glucose consumption, glucose uptake, and glycogen content in dexamethasone-induced HepG2 cells. The Western blotting results showed that gastrodin upregulated the expression of insulin receptors and ubiquitin-specific protease 4 (USP4) and increased the phosphorylation of GATA binding protein 1 (GATA1) and protein kinase B (AKT) in vivo and in vitro. Furthermore, gastrodin decreased the ubiquitin level of the insulin receptor via UPS4 and increased the binding of GATA1 to the USP4 promoter. Additionally, administration of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT signaling pathway inhibitors MK-2206 and LY294002 abolished the beneficial effects of gastrodin. Our results indicate that gastrodin promotes the phosphorylation of GATA1 via the PI3K/AKT pathway, enhances the transcriptional activity of GATA1, and then increases the expression level of USP4, thereby reducing the ubiquitination and degradation of insulin receptors and ultimately improving insulin resistance. Our study provides scientific evidence for the beneficial actions and underlying mechanism of gastrodin in the treatment of T2DM.
Keywords: AKT pathway; USP4; gastrodin; insulin resistance; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2021 Bai, Mo, Wang, Chen, Zhang, Guo and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




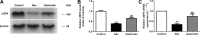

Similar articles
-
A review: Mechanism and prospect of gastrodin in prevention and treatment of T2DM and COVID-19.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 26;9(11):e21218. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21218. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37954278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eurocristatine, a plant alkaloid from Eurotium cristatum, alleviates insulin resistance in db/db diabetic mice via activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 15;887:173557. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173557. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32946868
-
Irisin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis and increases glycogen synthesis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic mice and hepatocytes.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Nov;129(10):839-50. doi: 10.1042/CS20150009. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26201094
-
The effect of Liuwei Dihuang decoction on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rats with insulin resistance.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Nov 4;192:382-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.024. Epub 2016 Jul 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27401286
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanistic Pathways Targeted by Natural Compounds in the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease.Molecules. 2022 Sep 21;27(19):6221. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196221. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.J Transl Med. 2025 Mar 25;23(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06255-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40133964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review: Mechanism and prospect of gastrodin in prevention and treatment of T2DM and COVID-19.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 26;9(11):e21218. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21218. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37954278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-Specific Proteases (USPs) and Metabolic Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 6;24(4):3219. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043219. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical significance of circulating long non-coding RNA SNHG1 in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with cell proliferation of pancreatic β-cell.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Oct 25;24(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01755-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 39455977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anyanwu G. O., Iqbal J., Khan S. U., Zaib S., Rauf K., Onyeneke C. E., et al. (2019). Antidiabetic Activities of Chloroform Fraction of Anthocleista Vogelii Planch Root Bark in Rats with Diet- and Alloxan-Induced Obesity-Diabetes. J. Ethnopharmacol 229, 293–302. 10.1016/j.jep.2018.10.021 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

