Trends of High-Impact Studies in Pharmacology and Pharmacy: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 34603039
- PMCID: PMC8481866
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.726668
Trends of High-Impact Studies in Pharmacology and Pharmacy: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
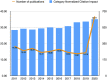
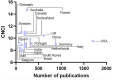
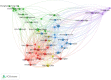
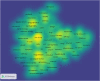
Objective: To investigate the trends of high-impact studies in pharmacology and pharmacy research and to provide evidence for future research in the field of pharmacology and pharmacy. Methods: A cross-sectional study was performed to understand the current status of high-impact studies (top 1%) in pharmacology and pharmacy research via InCites tool based on Web of Science Core Collection. VOSViewer software was used to visualize the results. The outcomes included development trends, countries, subject areas, research institutes, collaborative networks, and subject terms. Results: We found 4,273 high-impact (top 1%) studies between 2011 and 2020 in the field of pharmacology and pharmacy. The number of studies increased from 366 in 2011 to 510 in 2020. These studies were mainly distributed in the following Web of Science subject categories: pharmacology and pharmacy (n = 4,188); neurosciences (n = 397); chemistry, multidisciplinary (n = 359); chemistry, medicinal (n = 314); microbiology (n = 301); biotechnology and applied microbiology (n = 280). These studies were cited in 646,855 studies from more than 100 Web of Science subject categories, and studies in pharmacology pharmacy accounted for the largest share of these citations. The top three countries that contributed the highest number of studies were the United States, United Kingdom, and China. The top three institutions that contributed the highest number of studies in the United States were the University of California System, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and Harvard University. The top research collaborative circle was from universities in the United States. The top international collaborative circle was from universities from the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, and China. The subject-term analysis indicated that cancer was still the top disease, NF-κB was the top signaling pathway, and drug-delivery and nanoparticles were the top methods. Conclusion: The high-impact studies in pharmacology and pharmacy research have grown over time. The United States, the United Kingdom, and China are the top countries that contributed the high-impact studies. Cancer is still the greatest challenge in the field of disease treatment. It calls for more international collaboration in pharmacology and pharmacy research, which will help discover novel drugs.
Keywords: InCites; Web of Science; cancer; high-impact studies; pharmacology and pharmacy research; visual analysis.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Yang, Fan, Zhang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
High-impact papers in the field of anesthesiology: a 10-year cross-sectional study.Can J Anaesth. 2023 Feb;70(2):183-190. doi: 10.1007/s12630-022-02363-5. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Can J Anaesth. 2023. PMID: 36418743 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in high-impact papers in nursing research published from 2008 to 2018: A web of science-based bibliometric analysis.J Nurs Manag. 2020 Jul;28(5):1041-1052. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13038. Epub 2020 Jun 3. J Nurs Manag. 2020. PMID: 32458514
-
[Visualization analysis on treatment of coronavirus based on knowledge graph].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Mar;32(3):279-286. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200225-00200. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32385990 Chinese.
-
Mapping Trends in Moyamoya Angiopathy Research: A 10-Year Bibliometric and Visualization-Based Analyses of the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC).Front Neurol. 2021 Mar 2;12:637310. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.637310. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33737903 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Research on the Comorbidity of Pain and Inflammation.Pain Res Manag. 2021 Feb 17;2021:6655211. doi: 10.1155/2021/6655211. eCollection 2021. Pain Res Manag. 2021. PMID: 33680225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Correlation between Altmetric Attention Score and Traditional Bibliometrics in Top Nursing Journal Articles.J Nurs Manag. 2023 Feb 22;2023:2789960. doi: 10.1155/2023/2789960. eCollection 2023. J Nurs Manag. 2023. PMID: 40225615 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity of natural products against MDR bacteria: A scientometric visualization analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 26;13:1000974. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1000974. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36225591 Free PMC article.
-
High-impact papers in the field of anesthesiology: a 10-year cross-sectional study.Can J Anaesth. 2023 Feb;70(2):183-190. doi: 10.1007/s12630-022-02363-5. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Can J Anaesth. 2023. PMID: 36418743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen L. V., Jr. (2012). Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy: from the Past into the Future. Int. J. Pharm. Compd. 16 (5), 358–362. - PubMed
-
- Barnes J., Anderson L. A., Gibbons S., Phillipson J. D. (2005). Echinacea Species (Echinacea Angustifolia (DC.) Hell., Echinacea Pallida (Nutt.) Nutt.,Echinacea Purpurea (L.) Moench): a Review of Their Chemistry, Pharmacology and Clinical Properties. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 57 (8), 929–954. 10.1211/0022357056127 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

