The Long-Term Changes in Dynamic Risk and Protective Factors Over Time in a Nationwide Sample of Dutch Forensic Psychiatric Patients
- PMID: 34603110
- PMCID: PMC8481688
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.737846
The Long-Term Changes in Dynamic Risk and Protective Factors Over Time in a Nationwide Sample of Dutch Forensic Psychiatric Patients
Abstract
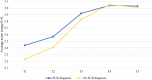
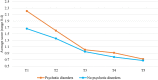
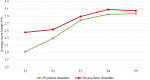
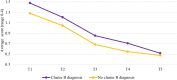
The long-term changes of dynamic risk and protective factors have rarely been studied in forensic psychiatric patients. We utilized a latent growth curve analysis to investigate trajectories of risk and protective factors over time in all 722 male forensic psychiatric patients who were unconditionally released between 2004 and 2014 from any of 12 Dutch forensic psychiatric centers (FPCs). The study covered the period from juridical observation until unconditional release. Moreover, we investigated whether these trajectories differ between patients depending on their psychiatric diagnosis namely substance use disorders (SUD), psychotic disorders, and cluster B personality disorders (PDs). In addition, we also investigated whether SUD may influence changes in risk and protective factors in a group of psychotic and cluster B PDs patients, respectively. Overall, findings suggest that all changes in dynamic risk and protective factors could be depicted by two phases of patients' stay in the FPCs. Specifically, most changes on dynamic risk and protective factors occurred at the beginning of treatment, that is, from the time of juridical assessment up to the time of unguided leave. Moreover, the moment of unguided leave could be considered the 'turning point' in the treatment of offenders. We also found that SUD and psychotic patients changed the most in the first phase of their stay, while cluster B PDs patients changed the most in the second phase. However, SUD did not modify changes in risk and protective factors in psychotic and cluster B PDs patients. These findings may help improve offender treatment and crime prevention strategies.
Keywords: cluster B personality disorders; forensic psychiatric patients; latent growth curve analysis; protective factors; psychotic disorders; risk factors; substance use disorder.
Copyright © 2021 Janković, Boxtel, Masthoff, Caluwé and Bogaerts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Trajectories of Dynamic Risk Factors During Forensic Treatment: Growth Trajectory of Clinical Risk Factors in a Sample of Dutch Forensic Patients.Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2020 Nov;64(15):1491-1513. doi: 10.1177/0306624X20909219. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2020. PMID: 32114842 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Network Structure and Changes of Clinical Risk and Protective Factors in a Nationwide Sample of Forensic Psychiatric Patients.Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2020 Nov;64(15):1533-1550. doi: 10.1177/0306624X20923256. Epub 2020 May 29. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2020. PMID: 32468885 Free PMC article.
-
Differences Between Readmitted and Non-readmitted Women in an Italian Forensic Unit: A Retrospective Study.Front Psychol. 2021 Oct 20;12:708873. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.708873. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34744870 Free PMC article.
-
[Alpha-interferon and mental disorders].Encephale. 2001 Jul-Aug;27(4):308-17. Encephale. 2001. PMID: 11686052 Review. French.
-
Sudden cardiac death: a nationwide cohort study among the young.Dan Med J. 2016 Dec;63(12):B5321. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27910804 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Dynamic Risk and Protective Factors in Predicting Violent Recidivism: Intellectual Ability as a Possible Moderator?Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2024 Feb;68(2-3):207-234. doi: 10.1177/0306624X221079695. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2024. PMID: 35227118 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of childhood maltreatment on aggression, criminal risk factors, and treatment trajectories in forensic psychiatric patients.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Nov 30;14:1128020. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1128020. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38098623 Free PMC article.
-
Change in Clinical Risk Factors During Stay and Treatment in a Penitentiary Psychiatric Center.Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2025 Jul;69(9):1333-1347. doi: 10.1177/0306624X241282279. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2025. PMID: 39377606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews DA, Bonta J. The Psychology of Criminal Conduct. New York, NY: Routledge; (2010).
-
- Ward T, Mann RE, Gannon TA. The good lives model of offender rehabilitation: clinical implications. Aggress Violent Behav. (2007) 12:87–107. 10.1016/j.avb.2006.03.004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

