Detection of Bioavailable Cadmium by Double-Color Fluorescence Based on a Dual-Sensing Bioreporter System
- PMID: 34603225
- PMCID: PMC8481780
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.696195
Detection of Bioavailable Cadmium by Double-Color Fluorescence Based on a Dual-Sensing Bioreporter System
Abstract
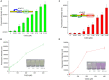
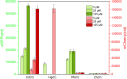
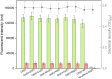
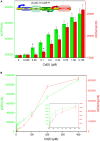
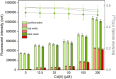
Cadmium (Cd) is carcinogenic to humans and can accumulate in the liver, kidneys, and bones. There is widespread presence of cadmium in the environment as a consequence of anthropogenic activities. It is important to detect cadmium in the environment to prevent further exposure to humans. Previous whole-cell biosensor designs were focused on single-sensing constructs but have had difficulty in distinguishing cadmium from other metal ions such as lead (Pb) and mercury (Hg). We developed a dual-sensing bacterial bioreporter system to detect bioavailable cadmium by employing CadC and CadR as separate metal sensory elements and eGFP and mCherry as fluorescent reporters in one genetic construct. The capability of this dual-sensing biosensor was proved to simultaneously detect bioavailable cadmium and its toxic effects using two sets of sensing systems while still maintaining similar specificity and sensitivity of respective signal-sensing biosensors. The productions of double-color fluorescence were directly proportional to the exposure concentration of cadmium, thereby serving as an effective quantitative biosensor to detect bioavailable cadmium. This novel dual-sensing biosensor was then validated to respond to Cd(II) spiked in environmental water samples. This is the first report of the development of a novel dual-sensing, whole-cell biosensor for simultaneous detection of bioavailable cadmium. The application of two biosensing modules provides versatile biosensing signals and improved performance that can make a significant impact on monitoring high concentration of bioavailable Cd(II) in environmental water to reduce human exposure to the harmful effects of cadmium.
Keywords: CadC; CadR; cadmium detection; fluorescent signal; whole-cell biosensor.
Copyright © 2021 Hui, Guo, Wu, Liu, Yang, Guo, Xie and Yi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Differential Detection of Bioavailable Mercury and Cadmium Based on a Robust Dual-Sensing Bacterial Biosensor.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 13;13:846524. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.846524. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35495723 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous detection of bioavailable arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils using dual-sensing bioreporters.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Apr;100(8):3713-22. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7338-6. Epub 2016 Feb 6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26852408
-
Development of a bioavailable Hg(II) sensing system based on MerR-regulated visual pigment biosynthesis.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 29;11(1):13516. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92878-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34188121 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Nanotechnology-Based Biosensors Development for Detection of Arsenic, Lead, Mercury, and Cadmium.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Feb 4;16:803-832. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S294417. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33568907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Usefulness of biomarkers of exposure to inorganic mercury, lead, or cadmium in controlling occupational and environmental risks of nephrotoxicity.Ren Fail. 1999 May-Jul;21(3-4):251-62. doi: 10.3109/08860229909085087. Ren Fail. 1999. PMID: 10416202 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic engineering of the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway toward a specific and sensitive inorganic mercury biosensor.RSC Adv. 2022 Dec 16;12(55):36142-36148. doi: 10.1039/d2ra06764a. eCollection 2022 Dec 12. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36545109 Free PMC article.
-
Use of whole-cell bioreporters to assess bioavailability of contaminants in aquatic systems.Front Chem. 2022 Sep 30;10:1018124. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1018124. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36247665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of Pb(II)-Specific E. coli-Based Biosensors by Engineering Regulatory Proteins and Host Cells.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 20;13:881050. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.881050. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35668759 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of environmental pollutant cadmium in water using a visual bacterial biosensor.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 27;12(1):6898. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11051-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35477977 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Detection of Bioavailable Mercury and Cadmium Based on a Robust Dual-Sensing Bacterial Biosensor.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 13;13:846524. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.846524. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35495723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amaro F., Turkewitz A. P., Martin-Gonzalez A., Gutierrez J. C. (2011). Whole-cell biosensors for detection of heavy metal ions in environmental samples based on metallothionein promoters from Tetrahymena thermophila. Microb. Biotechnol. 4 513–522. 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2011.00252.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

