Dynamics of Polarized Macrophages and Activated CD8+ Cells in Heart Tissue of Atlantic Salmon Infected With Piscine Orthoreovirus-1
- PMID: 34603301
- PMCID: PMC8481380
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.729017
Dynamics of Polarized Macrophages and Activated CD8+ Cells in Heart Tissue of Atlantic Salmon Infected With Piscine Orthoreovirus-1
Abstract
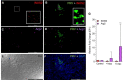
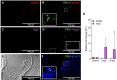
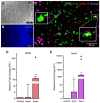
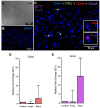
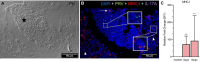
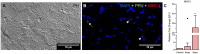
Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV-1) infection causes heart and skeletal muscle inflammation (HSMI) in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). The virus is also associated with focal melanized changes in white skeletal muscle where PRV-1 infection of macrophages appears to be important. In this study, we studied the macrophage polarization into M1 (pro-inflammatory) and M2 (anti-inflammatory) phenotypes during experimentally induced HSMI. The immune response in heart with HSMI lesions was characterized by CD8+ and MHC-I expressing cells and not by polarized macrophages. Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) assays revealed localization of PRV-1 in a few M1 macrophages in both heart and skeletal muscle. M2 type macrophages were widely scattered in the heart and were more abundant in heart compared to the skeletal muscle. However, the M2 macrophages did not co-stain for PRV-1. There was a strong cellular immune response to the infection in the heart compared to that of the skeletal muscle, seen as increased MHC-I expression, partly in cells also containing PRV-1 RNA, and a high number of cytotoxic CD8+ granzyme producing cells that targeted PRV-1. In skeletal muscle, MHC-I expressing cells and CD8+ cells were dispersed between myocytes, but these cells did not stain for PRV-1. Gene expression analysis by RT-qPCR complied with the FISH results and confirmed a drop in level of PRV-1 following the cell mediated immune response. Overall, the results indicated that M1 macrophages do not contribute to the initial development of HSMI. However, large numbers of M2 macrophages reside in the heart and may contribute to the subsequent fast recovery following clearance of PRV-1 infection.
Keywords: Atlantic salmon; Piscine orthoreovirus 1; cell mediated immunity; heart and skeletal muscle inflammation; macrophage polarization.
Copyright © 2021 Malik, Nyman, Wessel, Dahle and Rimstad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wessel O, Braaen S, Alarcon M, Haatveit H, Roos N, Markussen T, et al. . Infection With Purified Piscine Orthoreovirus Demonstrates a Causal Relationship With Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation in Atlantic Salmon. PloS One (2017) 12(8):e0183781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183781 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Svendsen J, Fritsvold C. The Health Situation in Norwegian Aquaculture. In: Chapter 45 Cardiomyopathy Syndrome (CMS) The Norwegian Veterinary Institute Report Series No 1b-2018. Oslo, Norway: The Norwegian Veterinary Institute; (2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

