Pertussis Vaccine Candidate Based on Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived From Biofilm Culture
- PMID: 34603306
- PMCID: PMC8479151
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.730434
Pertussis Vaccine Candidate Based on Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived From Biofilm Culture
Abstract
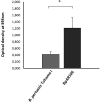
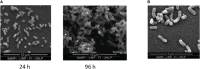
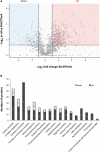
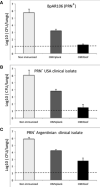
Outer membrane vesicles (OMV) derived from Bordetella pertussis-the etiologic agent of the resurgent disease called pertussis-are safe and effective in preventing bacterial colonization in the lungs of immunized mice. Vaccine formulations containing those OMV are capable of inducing a mixed Th1/Th2/Th17 profile, but even more interestingly, they may induce a tissue-resident memory immune response. This immune response is recommended for the new generation of pertussis-vaccines that must be developed to overcome the weaknesses of current commercial acellular vaccines (second-generation of pertussis vaccine). The third-generation of pertussis vaccine should also deal with infections caused by bacteria that currently circulate in the population and are phenotypically and genotypically different [in particular those deficient in the expression of pertactin antigen, PRN(-)] from those that circulated in the past. Here we evaluated the protective capacity of OMV derived from bacteria grown in biofilm, since it was observed that, by difference with older culture collection vaccine strains, circulating clinical B. pertussis isolates possess higher capacity for this lifestyle. Therefore, we performed studies with a clinical isolate with good biofilm-forming capacity. Biofilm lifestyle was confirmed by both scanning electron microscopy and proteomics. While scanning electron microscopy revealed typical biofilm structures in these cultures, BipA, fimbria, and other adhesins described as typical of the biofilm lifestyle were overexpressed in the biofilm culture in comparison with planktonic culture. OMV derived from biofilm (OMVbiof) or planktonic lifestyle (OMVplank) were used to formulate vaccines to compare their immunogenicity and protective capacities against infection with PRN(+) or PRN(-) B. pertussis clinical isolates. Using the mouse protection model, we detected that OMVbiof-vaccine was more immunogenic than OMVplank-vaccine in terms of both specific antibody titers and quality, since OMVbiof-vaccine induced antibodies with higher avidity. Moreover, when OMV were administered at suboptimal quantity for protection, OMVbiof-vaccine exhibited a significantly adequate and higher protective capacity against PRN(+) or PRN(-) than OMVplank-vaccine. Our findings indicate that the vaccine based on B. pertussis biofilm-derived OMV induces high protection also against pertactin-deficient strains, with a robust immune response.
Keywords: Bordetella pertussis; biofilm; outer membrane vesicles; planktonic; protection; vaccine.
Copyright © 2021 Carriquiriborde, Martin Aispuro, Ambrosis, Zurita, Bottero, Gaillard, Castuma, Rudi, Lodeiro and Hozbor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Pertussis Outer Membrane Vesicle-Based Vaccine Induces Lung-Resident Memory CD4 T Cells and Protection Against Bordetella pertussis, Including Pertactin Deficient Strains.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 26;9:125. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00125. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31106160 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal application of a bifunctional pertactin-RTX fusion antigen elicits protection of mouse airway mucosa against Bordetella pertussis colonization.mSphere. 2025 Apr 29;10(4):e0095924. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00959-24. Epub 2025 Mar 31. mSphere. 2025. PMID: 40162794 Free PMC article.
-
Pertactin negative Bordetella pertussis demonstrates higher fitness under vaccine selection pressure in a mixed infection model.Vaccine. 2015 Nov 17;33(46):6277-81. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.09.064. Epub 2015 Oct 2. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26432908
-
Bordetella pertussis and pertactin-deficient clinical isolates: lessons for pertussis vaccines.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014 Sep;13(9):1135-46. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2014.932254. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014. PMID: 24953157 Review.
-
Pertactin-Deficient Bordetella pertussis, Vaccine-Driven Evolution, and Reemergence of Pertussis.Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Jun;27(6):1561-1566. doi: 10.3201/eid2706.203850. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34014152 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding bacterial biofilms: From definition to treatment strategies.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Apr 6;13:1137947. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1137947. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37091673 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles and Immune Modulation of the Host.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Aug 24;13(9):752. doi: 10.3390/membranes13090752. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Latest Update on Outer Membrane Vesicles and Their Role in Horizontal Gene Transfer: A Mini-Review.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;13(11):860. doi: 10.3390/membranes13110860. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating proteomic data with metabolic modeling provides insight into key pathways of Bordetella pertussis biofilms.Front Microbiol. 2023 Aug 3;14:1169870. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1169870. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37601354 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Nanoparticles in Vaccine Development.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 23;10:867119. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.867119. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35402394 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

