PET Imaging of Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 34603323
- PMCID: PMC8481830
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.739130
PET Imaging of Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
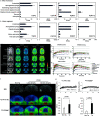
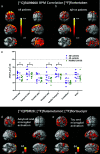
Neuroinflammation play an important role in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Advances in molecular imaging using positron emission tomography have provided insights into the time course of neuroinflammation and its relation with Alzheimer's disease central pathologies in patients and in animal disease models. Recent single-cell sequencing and transcriptomics indicate dynamic disease-associated microglia and astrocyte profiles in Alzheimer's disease. Mitochondrial 18-kDa translocator protein is the most widely investigated target for neuroinflammation imaging. New generation of translocator protein tracers with improved performance have been developed and evaluated along with tau and amyloid imaging for assessing the disease progression in Alzheimer's disease continuum. Given that translocator protein is not exclusively expressed in glia, alternative targets are under rapid development, such as monoamine oxidase B, matrix metalloproteinases, colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor, imidazoline-2 binding sites, cyclooxygenase, cannabinoid-2 receptor, purinergic P2X7 receptor, P2Y12 receptor, the fractalkine receptor, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2, and receptor for advanced glycation end products. Promising targets should demonstrate a higher specificity for cellular locations with exclusive expression in microglia or astrocyte and activation status (pro- or anti-inflammatory) with highly specific ligand to enable in vivo brain imaging. In this review, we summarised recent advances in the development of neuroinflammation imaging tracers and provided an outlook for promising targets in the future.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; TSPO (18 kDa translocator protein); amyloid (A) 42; astrocyte; microglia; neuroinflammation; positron emission tomography (PET); tau.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Ji, Kong, Qin, Ren, Guan and Ni.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

