A Role of Variance in Interferon Genes to Disease Severity in COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 34603376
- PMCID: PMC8484761
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.709388
A Role of Variance in Interferon Genes to Disease Severity in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
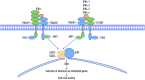
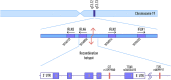
The rapid rise and global consequences of the novel coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) have again brought the focus of the scientific community on the possible host factors involved in patient response and outcome to exposure to the virus. The disease severity remains highly unpredictable, and individuals with none of the aforementioned risk factors may still develop severe COVID-19. It was shown that genotype-related factors like an ABO Blood Group affect COVID-19 severity, and the risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2 was higher for patients with blood type A and lower for patients with blood type O. Currently it is not clear which specific genes are associated with COVID-19 severity. The comparative analysis of COVID-19 and other viral infections allows us to predict that the variants within the interferon pathway genes may serve as markers of the magnitude of immune response to specific pathogens. In particular, various members of Class III interferons (lambda) are reviewed in detail.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; differential activity; interferons; signaling; type I interferon.
Copyright © 2021 Gozman, Perry, Nikogosov, Klabukov, Shevlyakov and Baranova.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors DN, AS, and AB were employed by the company Atlas Biomed Group Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Agwa S. H. A., Kamel M. M., Elghazaly H., Abd Elsamee A. M., Hafez H., Girgis S. A., et al. (2021). Association between Interferon-Lambda-3 Rs12979860, TLL1 Rs17047200 and DDR1 Rs4618569 Variant Polymorphisms with the Course and Outcome of SARS-CoV-2 Patients. Genes 12 (6), 830. 10.3390/genes12060830 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous