Review of Anopheles Mosquito Species, Abundance, and Distribution in Ethiopia
- PMID: 34603455
- PMCID: PMC8486561
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6726622
Review of Anopheles Mosquito Species, Abundance, and Distribution in Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Malaria is a major mosquito-borne disease in Ethiopia, and it is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality. Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax are the two malaria-causing parasitic species commonly known to cause human malaria in Ethiopia. To better manage and control vectors transmitting malaria parasites, the abundance, distribution, and updated annotated list of Anopheles species present in Ethiopia are very important.
Methods: In order to compile a list of the species recorded in Ethiopia, 33 original research articles were collected. This work gives an updated list of Anopheles mosquito species in Ethiopia and their abundance, distribution, and composition.
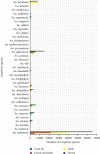
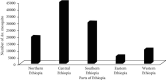
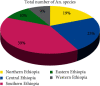
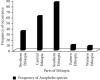
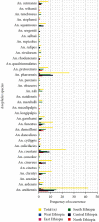
Results: According to this review, 110305 Anopheles mosquitoes were collected and 35 Anopheles species were recorded in different parts of Ethiopia. A. arabiensis was the most abundant when compared to other species, whereas A. maculipalpis and A. wilsonii were the least abundant species. The most abundant Anopheles species was recorded in central and the least abundant, from eastern Ethiopia. The second, third, and fourth abundant species were also collected from southern, northern, and western parts of Ethiopia.
Copyright © 2021 Fasil Adugna et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
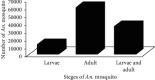
Similar articles
-
Molecular and morphological identification of suspected Plasmodium vivax vectors in Central and Eastern Sudan.Malar J. 2021 Mar 4;20(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12936-021-03671-9. Malar J. 2021. PMID: 33663534 Free PMC article.
-
Species composition, blood meal hosts and Plasmodium infection rates of Anopheles mosquitoes in Ghibe River Basin, southwestern Ethiopia.Parasit Vectors. 2019 May 23;12(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3499-3. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31122286 Free PMC article.
-
Similar trends of susceptibility in Anopheles arabiensis and Anopheles pharoensis to Plasmodium vivax infection in Ethiopia.Parasit Vectors. 2016 Oct 18;9(1):552. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1839-0. Parasit Vectors. 2016. PMID: 27756355 Free PMC article.
-
Malaria entomological profile in Tanzania from 1950 to 2010: a review of mosquito distribution, vectorial capacity and insecticide resistance.Tanzan J Health Res. 2011 Dec;13(5 Suppl 1):319-31. Tanzan J Health Res. 2011. PMID: 26591987 Review.
-
Malaria Prevalence and Distribution of Plasmodium Species in Southern Region of Ethiopia.J Parasitol Res. 2022 Jun 23;2022:5665660. doi: 10.1155/2022/5665660. eCollection 2022. J Parasitol Res. 2022. PMID: 35782658 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic review of sporozoite infection rate of Anopheles mosquitoes in Ethiopia, 2001-2021.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Nov 27;16(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06054-y. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 38008761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population genetic structure and phylogenetic analysis of Anopheles hyrcanus (Diptera: Culicidae) inferred from DNA sequences of nuclear ITS2 and the mitochondrial COI gene in the northern part of Iran.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jul 23;24(1):724. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09626-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39044181 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the mosquito-haemosporidian parasite-bird host network in the southwestern Iberian Peninsula: insights into malaria infections, mosquito community and feeding preferences.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Nov 1;16(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05964-1. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37915080 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Plasmodium Sporozoite Infection Rates in Primary and Secondary Malaria Vectors in Anopheles stephensi-Infested Areas of Ethiopia.Insects. 2025 Apr 27;16(5):462. doi: 10.3390/insects16050462. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40429175 Free PMC article.
-
A Nanoliposomal Gel Containing Cinnamomum zeylanicum Essential Oil with Effective Repellent against the Main Malaria Vector Anopheles stephensi.Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2022 Jun 22;2022:1645485. doi: 10.1155/2022/1645485. eCollection 2022. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35784810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaugler R. Medical Entomology for Students . Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 2016.
-
- Mullen G. R., Durden L. A. Medical and Veterinary Entomology . Cambridge, MA, USA: Academic Press; 2009.
-
- Goutam Chandra G. C., Anupam Ghosh A. G., Indranil Bhattacharjee I. B., Ghosh S. K. Biological and Environmental Control of Disease Vectors . Boston, MA, USA: CABI; 2013. Use of larvivorous fish in biological and environmental control of disease vectors; pp. 25–41. - DOI
-
- Gubler D. J. Vector Biol, Ecol Cont . New York, NY, USA: Springer; 2010. The global threat of emergent/re-emergent vector-borne diseases; pp. 39–62. - DOI
-
- Molavi A. Africa’s malaria death toll still outrageously high. Nat Geo News . 2003;12
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

