Exploring the Potential Mechanism of Shennao Fuyuan Tang for Ischemic Stroke Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
- PMID: 34603472
- PMCID: PMC8486536
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6015702
Exploring the Potential Mechanism of Shennao Fuyuan Tang for Ischemic Stroke Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
Abstract
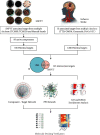
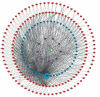
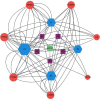
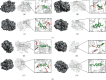
Methods: Screen the biologically active components and potential targets of SNFYT through Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP), Traditional Chinese Medicines Integrated Database (TCMID), and related literature. In addition, DrugBank, OMIM, DisGeNET, and the Therapeutic Target Database were searched to explore the therapeutic targets of IS. The cross-targets of SNFYT potential targets and IS treatment targets were taken as candidate gene targets, and GO and KEGG enrichment analyses were performed on the candidate targets. On this basis, the SNFYT-component-target network and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network were constructed using Cytoscape 3.7.2. Finally, AutoDock was used to verify the molecular docking of core components and core targets.
Results: We screened out 95 potentially active components and 143 candidate targets. SNFYT-component-target network, PPI network, and Cytoscape analysis identified four core active ingredients and 14 core targets. GO enrichment analyzed 2333 biological processes, 79 cell components, and 149 molecular functions. There are 170 KEGG-related signal pathways (P < 0.05), including the IL-17 signal pathway, TNF signal pathway, and HIF-1 signal pathway. The molecular docking results of the core components and the core targets showed good binding power.
Conclusions: SNFYT may achieve the effect of treating ischemic stroke through its anti-inflammatory effect through a signal pathway with core targets as the core.
Copyright © 2021 Jia Min Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Exploring the mechanisms of Jujing pill on varicocele-associated male infertility via network pharmacology and molecular docking technology].Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2023 Aug;29(8):688-697. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2023. PMID: 38619514 Chinese.
-
Exploring the Mechanisms of Self-made Kuiyu Pingchang Recipe for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis and Irritable Bowel Syndrome using a Network Pharmacology-based Approach and Molecular Docking.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(5):534-550. doi: 10.2174/1573409919666230515103224. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37190808
-
Research on the Regulatory Mechanism of Ginseng on the Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal Cancer based on Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics Validation.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(5):486-500. doi: 10.2174/1573409919666230607103721. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37287284
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking study on the mechanism of colorectal cancer treatment using Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 14;16(6):e0252508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252508. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34125845 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of Wuling Capsules against hepatic fibrosis based on network pharmacology and animal experiments].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Oct;48(19):5365-5376. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230707.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38114126 Chinese.
Cited by
-
The impact of inflammation and iron metabolism on gene expression alterations in ischemic stroke: a bioinformatics approach.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 30;15(1):15233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00369-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40307317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DALYs G. B. D., Collaborators H. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet . 2017;390(10100):1260–1344. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32335-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

