Assessment of the Link of ABCB1 and NR3C1 gene polymorphisms with the prednisolone resistance in pediatric nephrotic syndrome patients of Bangladesh: A genotype and haplotype approach
- PMID: 34603785
- PMCID: PMC8463901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.02.001
Assessment of the Link of ABCB1 and NR3C1 gene polymorphisms with the prednisolone resistance in pediatric nephrotic syndrome patients of Bangladesh: A genotype and haplotype approach
Abstract
Introduction: Nephrotic syndrome is a common pediatric kidney disease. Investigations on several genetic polymorphisms revealed an inconsistent influence on the resistance of patients to steroids.
Objectives: This study aimed to identify the association of ABCB1 (1236C > T, 2677G > T, 3435C > T), NR3C1 (rs10482634, rs6877893), and CYP3A5 (CYP3A5*3) gene polymorphism as well as sociodemographic and clinicopathological parameters with the risk of developing prednisolone resistance in pediatric patients with nephrotic syndrome.
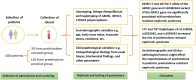
Methods: A case-control analysis was performed on 180 nephrotic syndrome patients. Among them, 30 patients were classified as prednisolone resistant group, and 150 were classified as prednisolone sensitive group. Genotyping was performed by the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method.
Results: No significant association of 1236C > T polymorphism with the risk of prednisolone resistance (p > 0.05) was found. The GT heterozygous of 2677G > T was found to be significantly associated with the development of prednisolone resistance (OR = 3.9, p = 0.034). In the case of 3435C > T, a statistically significant association was observed in TC heterozygous and TT mutant homozygous genotypes (OR = 0.38, p = 0.047; OR = 3.06, p = 0.038, respectively) with prednisolone resistance. For rs10482634 polymorphism, the AG heterozygous and AG+GG genotypes were significantly linked with prednisolone resistance (OR = 2.40, p = 0.033; OR = 2.36, p = 0.034, respectively). We found no association with the risk of prednisolone resistance with rs6877893 and CYP3A5*3 polymorphism (p > 0.05). CTC and TGT haplotypes of ABCB1 and GA haplotype of NR3C1 were also associated with the increased risk of pediatric prednisolone resistance (OR = 4.47, p = 0.0003; OR = 2.71, p = 0.03; and OR = 4.22, p = 0.022, consecutively). We also observed the correlation of different sociodemographic and clinicopathological factors with prednisolone resistance in pediatric nephrotic syndrome.
Conclusion: Our findings showed a significant association of ABCB1 and NR3C1 gene polymorphisms with prednisolone resistant pediatric nephrotic syndrome.
Keywords: 95%CI, 95% confidence intervals; ABCB1; CYP3A5; GC, Glucocorticoids; GR, Glucocorticoid receptor; HWE, Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium; LD, Linkage disequilibrium; MDR1, multidrug resistance gene 1; MesPGN, mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis; NR3C1; NR3C1, nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 1; NS, Nephrotic syndrome; Nephrotic syndrome; OR, odds ratio; P-gp, Permeability glycoprotein; PCR-RFLP, polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism; PR, Prednisolone resistance; PRG, Prednisolone resistance group; PRNS, Prednisolone resistance nephrotic syndrome; PSG, Prednisolone sensitive group; Pharmacogenetics; Prednisolone resistance; SRNS, steroid-resistance nephrotic syndrome; SSNS, Steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Cairo University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NR3C1 variants and glucocorticoid response in childhood nephrotic syndrome in North India.BMC Nephrol. 2025 May 14;26(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04173-5. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40369478 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-drug resistance-1 gene polymorphisms in nephrotic syndrome: impact on susceptibility and response to steroids.Gene. 2013 Nov 10;530(2):201-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.045. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23994685
-
ABCB1 polymorphisms and steroid treatment in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome.Br J Biomed Sci. 2017 Jan;74(1):36-41. doi: 10.1080/09674845.2016.1220707. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Br J Biomed Sci. 2017. PMID: 27719329
-
The role of ABCB1 gene polymorphisms in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: Evidence from a meta-analysis of steroid-receiving patients.J Gene Med. 2022 Jul;24(7):e3436. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3436. Epub 2022 Jun 25. J Gene Med. 2022. PMID: 35697639 Review.
-
Pharmacology and pharmacogenetics of prednisone and prednisolone in patients with nephrotic syndrome.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Mar;34(3):389-403. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-3929-z. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 29549463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Individualized medication based on pharmacogenomics and treatment progress in children with IgAV nephritis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 22;13:956397. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.956397. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35935867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NR3C1 variants and glucocorticoid response in childhood nephrotic syndrome in North India.BMC Nephrol. 2025 May 14;26(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04173-5. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40369478 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in drug metabolism genes predict the risk of refractory myasthenia gravis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Nov;10(21):1155. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2543. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36467365 Free PMC article.
-
WTAP-mediated m6A modification promotes drug sensitivity by regulating NR3C1 in prostate cancer.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Jul 8. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2776-3. Online ahead of print. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650812
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Validation to Explore the Pharmacological Mechanism of Zhuling Decoction against Nephrotic Syndrome.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(28):2244-2256. doi: 10.2174/0113816128305808240529115047. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38910482
References
-
- Nawaz Z., Mushtaq F., Mousa D. Pattern of glomerular disease in the Saudi population: A single-center, five-year retrospective study. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant. 2013;24(6):1265. - PubMed
-
- Bagga A. Management of steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome. Indian Pediatr. 2009;46(1) - PubMed
-
- Levine S.A. In: Brenner & Rector's The Kidney. 7th ed. Brenner B.M., Floyd C., editors. WB Saunders; Philadelphia: 2003. Nephrotic Syndrome; pp. 297–313.
-
- Gordillo R., Spitzer A. The nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Rev. 2009;30(3):94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous