Sex- and stage-dependent expression patterns of odorant-binding and chemosensory protein genes in Spodoptera exempta
- PMID: 34603852
- PMCID: PMC8445084
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12132
Sex- and stage-dependent expression patterns of odorant-binding and chemosensory protein genes in Spodoptera exempta
Abstract
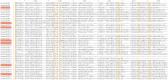
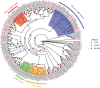
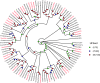
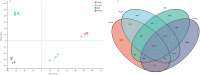
As potential molecular targets for developing novel pest management strategies, odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) and chemosensory proteins (CSPs) have been considered to initiate odor recognition in insects. Herein, we investigated the OBPs and CSPs in a major global crop pest (Spodoptera exempta). Using transcriptome analysis, we identified 40 OBPs and 33 CSPs in S. exempta, among which 35 OBPs and 29 CSPs had intact open reading frames. Sequence alignment indicated that 30 OBPs and 23 CSPs completely contained the conserved cysteines. OBPs of lepidopteran insects usually belonged to classical, minus-C, and plus-C groups. However, phylogenetic analyses indicated that we only identified 28 classical and seven minus-C OBPs in S. exempta, suggesting that we might have missed some typical OBPs in lepidopteran insects, probably due to their low expression levels. All of the CSPs from S. exempta clustered with the orthologs of other moths. The identification and expression of the OBPs and CSPs were well studied in insect adults by transcriptional analyses, and herein we used samples at different stages to determine the expression of OBPs and CSPs in S. exempta. Interestingly, our data indicated that several OBPs and CSPs were especially or more highly expressed in larvae or pupae than other stages, including three exclusively (SexeOBP13, SexeOBP16 and SexeCSP23) and six more highly (SexeOBP15, SexeOBP37, SexeCSP4, SexeCSP8, SexeCSP19, and SexeCSP33) expressed in larvae, two exclusively (SexeCSP6 and SexeCSP20) and three more highly (SexeOBP18, SexeCSP17, and SexeCSP26) expressed in pupae. Usually, OBPs and CSPs had both male- and female-biased expression patterns in adult antennae. However, our whole-body data indicated that all highly expressed OBPs and CSPs in adults were male-biased or did not differ, suggesting diverse OBP and CSP functions in insect adults. Besides identifying OBPs and CSPs as well as their expression patterns, these results provide a molecular basis to facilitate functional studies of OBPs and CSPs for exploring novel management strategies to control S. exempta.
Keywords: Chemosensory protein; Gene expression; Odorant-binding protein; Spodoptera exempta; Transcriptome.
©2021 Dong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Chen CJ, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He YH, Xia R. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant. 2000;13:1194–1202. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

