The prospective of Artificial Intelligence in COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 34603925
- PMCID: PMC8476291
- DOI: 10.1007/s12553-021-00601-2
The prospective of Artificial Intelligence in COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
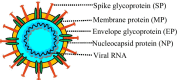
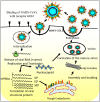
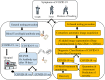
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a major threat throughout the world. The latest advancements in the field of computational techniques based on Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and Big Data can help in detecting, monitoring and forecasting the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic. We aim to review the detection of the COVID-19 pandemic empowered by AI, major implications, challenges and the future of smart health care at a glance. The AI plays a pioneering role in rapid and improved detection of the disease. It helps in modeling the disease activity and predicting the severity for better decision making and preparedness by healthcare authorities and policymakers. It is a promising technology for automatic and fully transparent monitoring system to track and treat the patients remotely without spreading the virus to others. The future application areas of AI-based healthcare are also identified. The role of AI in tackling the COVID-19 pandemic is reviewed in this paper. AI proves beneficial in early detection with improved results. It also provides solution for contact tracing, prediction, drug development thus reducing the workload of medical industry.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence; COVID-19; Coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2.
© IUPESM and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Informed consentThe authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest. I further confirm that this article is original and has not been published elsewhere nor is it currently under consideration for publication elsewhereConflict of interest ◦ All authors have participated in (a) conception and design, or analysis and interpretation of the data; (b) drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; and (c) approval of the final version. ◦ This manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is under review at, another journal or other publishing venue. ◦ The authors have no affiliation with any organization with a direct or indirect financial interest in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript ◦ The following authors have affiliations with organizations with direct or indirect financial interest in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript:
Figures
References
-
- World meter hwwic. 2020 May 8.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
