Improved detection of solitary pulmonary nodules on radiographs compared with deep bone suppression imaging
- PMID: 34603989
- PMCID: PMC8408784
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-20-1346
Improved detection of solitary pulmonary nodules on radiographs compared with deep bone suppression imaging
Abstract
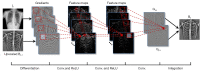
Background: The present study aimed to investigate whether deep bone suppression imaging (BSI) could increase the diagnostic performance for solitary pulmonary nodule detection compared with digital tomosynthesis (DTS), dual-energy subtraction (DES) radiography, and conventional chest radiography (CCR).
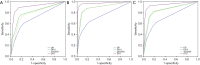
Methods: A total of 256 patients (123 with a solitary pulmonary nodule, 133 with normal findings) were included in the study. The confidence score of 6 observers determined the presence or absence of pulmonary nodules in each patient. These were first analyzed using a CCR image, then with CCR plus deep BSI, then with CCR plus DES radiography, and finally with DTS images. Receiver-operating characteristic curves were used to evaluate the performance of the 6 observers in the detection of pulmonary nodules.
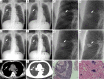
Results: For the 6 observers, the average area under the curve improved significantly from 0.717 with CCR to 0.848 with CCR plus deep BSI (P<0.01), 0.834 with CCR plus DES radiography (P<0.01), and 0.939 with DTS (P<0.01). Comparisons between CCR and CCR plus deep BSI found that the sensitivities of the assessments by the 3 residents increased from 53.2% to 69.5% (P=0.014) for nodules located in the upper lung field, from 30.6% to 44.6% (P=0.015) for nodules that were partially/completely obscured by the bone, and from 33.2% to 45.8% (P=0.006) for nodules <10 mm.
Conclusions: The deep BSI technique can significantly increase the sensitivity of radiology residents for solitary pulmonary nodules compared with CCR. Increased detection was seen mainly for smaller nodules, nodules with partial/complete obscuration, and nodules located in the upper lung field.
Keywords: Bone suppression; digital tomosynthesis; dual-energy subtraction; solitary pulmonary nodules.
2021 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/qims-20-1346). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The advantage of digital tomosynthesis for pulmonary nodule detection concerning influence of nodule location and size: a phantom study.Clin Radiol. 2017 Sep;72(9):796.e1-796.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2017.03.022. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Clin Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28454640
-
Bone suppressed images improve radiologists' detection performance for pulmonary nodules in chest radiographs.Eur J Radiol. 2013 Dec;82(12):2399-405. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.09.016. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Eur J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24113431
-
Role of digital tomosynthesis and dual energy subtraction digital radiography in detecting pulmonary nodules.Eur J Radiol. 2015 Jul;84(7):1383-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.03.020. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Eur J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25892052
-
Comparison of chest dual-energy subtraction digital tomosynthesis and dual-energy subtraction radiography for detection of pulmonary nodules: initial evaluations in human clinical cases.Acad Radiol. 2013 Nov;20(11):1357-63. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2013.08.006. Acad Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24119347
-
Bone Suppression on Chest Radiographs for Pulmonary Nodule Detection: Comparison between a Generative Adversarial Network and Dual-Energy Subtraction.Korean J Radiol. 2022 Jan;23(1):139-149. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2021.0146. Korean J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34983100 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of one-shot dual-energy subtraction chest radiography with flat-panel detector in distinguishing between calcified and non-calcified nodules.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 12;13(1):9548. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36785-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37308582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oda S, Awai K, Funama Y, Utsunomiya D, Yanaga Y, Kawanaka K, Nakaura T, Hirai T, Murakami R, Nomori H, Yamashita Y. Detection of small pulmonary nodules on chest radiographs: efficacy of dual-energy subtraction technique using flat-panel detector chest radiography. Clin Radiol 2010;65:609-15. 10.1016/j.crad.2010.02.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schalekamp S, van Ginneken B, Meiss L, Peters-Bax L, Quekel LG, Snoeren MM, Tiehuis A M, Wittenberg R, Karssemeijer N, Schaefer-Prokop CM. Bone suppressed images improve radiologists' detection performance for pulmonary nodules in chest radiographs. Eur J Radiol 2013;82:2399-405. 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.09.016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Szucs-Farkas Z, Schick A, Cullmann JL, Ebner L, Megyeri B, Vock P, Christe A. Comparison of dual-energy subtraction and electronic bone suppression combined with computer-aided detection on chest radiographs: effect on human observers' performance in nodule detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013;200:1006-13. 10.2214/AJR.12.8877 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
