Radiomics feature reliability assessed by intraclass correlation coefficient: a systematic review
- PMID: 34603997
- PMCID: PMC8408801
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-21-86
Radiomics feature reliability assessed by intraclass correlation coefficient: a systematic review
Abstract
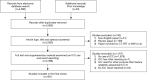
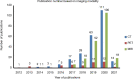
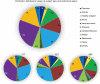
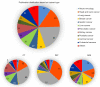
Radiomics research is rapidly growing in recent years, but more concerns on radiomics reliability are also raised. This review attempts to update and overview the current status of radiomics reliability research in the ever expanding medical literature from the perspective of a single reliability metric of intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). To conduct this systematic review, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed. After literature search and selection, a total of 481 radiomics studies using CT, PET, or MRI, covering a wide range of subject and disease types, were included for review. In these highly heterogeneous studies, feature reliability to image segmentation was much more investigated than reliability to other factors, such as image acquisition, reconstruction, post-processing, and feature quantification. The reported ICCs also suggested high radiomics feature reliability to image segmentation. Image acquisition was found to introduce much more feature variability than image segmentation, in particular for MRI, based on the reported ICC values. Image post-processing and feature quantification yielded different levels of radiomics reliability and might be used to mitigate image acquisition-induced variability. Some common flaws and pitfalls in ICC use were identified, and suggestions on better ICC use were given. Due to the extremely high study heterogeneities and possible risks of bias, the degree of radiomics feature reliability that has been achieved could not yet be safely synthesized or derived in this review. More future researches on radiomics reliability are warranted.
Keywords: Radiomics; intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC); oncology; quantitative imaging; reliability.
2021 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/qims-21-86). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. JY serves as an unpaid Associate Editor of Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability of MRI radiomics features in MR-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Repeatability, reproducibility, and within-subject agreement.Med Phys. 2021 Nov;48(11):6976-6986. doi: 10.1002/mp.15232. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34562286
-
Acquisition repeatability of MRI radiomics features in the head and neck: a dual-3D-sequence multi-scan study.Vis Comput Ind Biomed Art. 2022 Apr 1;5(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s42492-022-00106-3. Vis Comput Ind Biomed Art. 2022. PMID: 35359245 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the reliable feature change in longitudinal radiomics studies: A methodological approach using the reliable change index.Med Phys. 2023 Feb;50(2):958-969. doi: 10.1002/mp.16046. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36251320
-
Accuracy and Reliability of Imaging Modalities for the Diagnosis and Quantification of Hill-Sachs Lesions: A Systematic Review.Arthroscopy. 2021 Jan;37(1):391-401. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Arthroscopy. 2021. PMID: 32798670
-
Radiomics in nuclear medicine: robustness, reproducibility, standardization, and how to avoid data analysis traps and replication crisis.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Dec;46(13):2638-2655. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04391-8. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31240330 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic performance of MRI-based radiomics models using machine learning approaches for the triple classification of parotid tumors.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 22;10(17):e36601. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36601. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39263059 Free PMC article.
-
Appropriate pelvic obliquity measurement method in Lenke type 5C adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a preliminary study.J Spine Surg. 2024 Jun 21;10(2):255-263. doi: 10.21037/jss-23-138. Epub 2024 Jun 13. J Spine Surg. 2024. PMID: 38974492 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics from multisite MRI and clinical data to predict clinically significant prostate cancer.Acta Radiol. 2024 Mar;65(3):307-317. doi: 10.1177/02841851231216555. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Acta Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38115809 Free PMC article.
-
Repeatability of radiomics studies in colorectal cancer: a systematic review.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 14;23(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02743-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37059990 Free PMC article.
-
Interobserver delineation variability of computed tomography-based radiomic features of the parotid gland.Radiat Oncol J. 2024 Mar;42(1):63-73. doi: 10.3857/roj.2023.00605. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Radiat Oncol J. 2024. PMID: 38549385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, van Stiphout RG, Granton P, Zegers CM, Gillies R, Boellard R, Dekker A, Aerts HJ. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer 2012;48:441-6. 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
