Relationship between cortisol, Interleukin-6 and homocysteine in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 34604020
- PMCID: PMC8473151
- DOI: 10.5339/qmj.2021.33
Relationship between cortisol, Interleukin-6 and homocysteine in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Objective: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterised by progressive cognitive decline due to neurodegeneration. Over activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, oxidative stress and inflammation potentially damage the neuronal system, affecting cognition.
Aim: This study aimed to assess the relationship between serum cortisol, Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and homocysteine (Hcy) levels in AD.
Methods: Case-Control observational study consisting of 71 patients with AD and 70 healthy controls above 60 years of age. Serum samples were analysed for cortisol, IL-6 and Hcy levels using chemiluminescence immunoassay (Immulite 1000) technique. Cognitive functions were measured using the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) Score. AD subjects were categorised based on the modified Kuppuswamy socioeconomic status scale. Statistical evaluation was conducted using SPSS Statistics software. Group data were analysed using a two-tailed Student's t-test, analysis of variance (ANOVA), the Mann-Whitney U test and Pearson's correlation test.
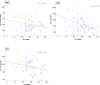
Results: Serum cortisol, IL-6 and Hcy levels were significantly increased (p < 0.01) in AD (cortisol: 19.69 ± 8.96 ug/dl; IL-6: 10.27 ± 2.76 pg/ml; Hcy: 23.29 ± 3.81 μmol/l), as compared with the controls (cortisol: 13.37 ± 5.59 ug/dl; IL-6: 3.37 ± 0.79 pg/ml; Hcy: 8.25 ± 2.36 μmol/l). MMSE scores in AD were negatively correlated with cortisol, IL-6 and Hcy levels.
Conclusions: Serum cortisol, IL-6 and Hcy levels are independent biomarkers for AD progression. Hypercortisolaemia, hyperhomocysteinemia and inflammation play important roles in AD-related cognitive dysfunction and are interlinked.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Interleukin-6; cortisol; homocysteine.
© 2021 Yeram, Dalvi, Mankeshwar, Patil, Kale, Jagiasi, Abichandani, licensee HBKU Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The clinical studies of hyperhomocysteinemia and Alzheimer's disease].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Mar;29(2):116-8, 127. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23833960 Chinese.
-
Elevated serum homocysteine level is not associated with serum C-reactive protein in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009 Dec;116(12):1651-6. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0325-7. Epub 2009 Oct 7. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009. PMID: 19809863
-
Ameliorative Effect of Acetyl L-carnitine in Alzheimer's Disease via Downregulating of Homocysteine Levels in Hyperhomocysteinemia Induced Cognitive Deficit in Mouse Model.Drug Metab Lett. 2021;14(3):219-231. doi: 10.2174/1872312814666211209102136. Drug Metab Lett. 2021. PMID: 34886786
-
Blood and CSF Homocysteine Levels in Alzheimer's Disease: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of Case-Control Studies.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022 Oct 17;18:2391-2403. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S383654. eCollection 2022. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022. PMID: 36276430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homocysteine and Folic Acid: Risk Factors for Alzheimer's Disease-An Updated Meta-Analysis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 May 26;13:665114. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.665114. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34122042 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cognitive Dysfunction and Affective Mood Disorder Screening in Patients With Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Protocol for a Prospective Case-Control Study.JMIR Res Protoc. 2023 Oct 12;12:e50546. doi: 10.2196/50546. JMIR Res Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37824197 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 Enhances the Negative Impact of Cortisol on Cognition among Community-Dwelling Older People without Dementia.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Mar 25;11(7):951. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11070951. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046878 Free PMC article.
-
Early Benefits with Potential Long-Term Risks of a Comprehensive Intervention on Serum Cortisol Levels and Cognitive Performance in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2023 Dec 29;7(1):1445-1453. doi: 10.3233/ADR-230125. eCollection 2023. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2023. PMID: 38225963 Free PMC article.
-
MCP-1 levels in astrocyte-derived exosomes are changed in preclinical stage of Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurol. 2023 Mar 20;14:1119298. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1119298. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37021284 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid levels of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones in MCI and dementia due to Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review.Dement Neuropsychol. 2023 Dec 11;17:e20230031. doi: 10.1590/1980-5764-DN-2023-0031. eCollection 2023. Dement Neuropsychol. 2023. PMID: 38089172 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chang YS, Wu YH, Wang CJ, Tang SH, Chen HL. The relationship between thyroid status, cortisol level, cognition and neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with Alzheimer disease. Neuropsychiatry. 2018;08(3):786–93.
-
- Lara VP, Caramelli P, Teixeira AL, Barbosa MT, Carmona KC, Carvalho MG, et al. High cortisol levels are associated with cognitive impairment no-dementia (CIND) and dementia. Clin Chim Acta. 2013;423:18–22. - PubMed
-
- Dhikav V, Sharma L, Mishra P, Sharma N, Anand KS, Duraisamy S, et al. Basal serum cortisol levels, depression and medial temporal lobe atrophy in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. J Depress Ther. 2016;1(1):25–31.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources