Neurofibromatosis: Molecular Pathogenesis and Natural Compounds as Potential Treatments
- PMID: 34604034
- PMCID: PMC8485038
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.698192
Neurofibromatosis: Molecular Pathogenesis and Natural Compounds as Potential Treatments
Abstract
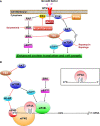
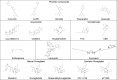
The neurofibromatosis syndromes, including NF1, NF2, and schwannomatosis, are tumor suppressor syndromes characterized by multiple nervous system tumors, particularly Schwann cell neoplasms. NF-related tumors are mainly treated by surgery, and some of them have been treated by but are refractory to conventional chemotherapy. Recent advances in molecular genetics and genomics alongside the development of multiple animal models have provided a better understanding of NF tumor biology and facilitated target identification and therapeutic evaluation. Many targeted therapies have been evaluated in preclinical models and patients with limited success. One major advance is the FDA approval of the MEK inhibitor selumetinib for the treatment of NF1-associated plexiform neurofibroma. Due to their anti-neoplastic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, selected natural compounds could be useful as a primary therapy or as an adjuvant therapy prior to or following surgery and/or radiation for patients with tumor predisposition syndromes, as patients often take them as dietary supplements and for health enhancement purposes. Here we review the natural compounds that have been evaluated in NF models. Some have demonstrated potent anti-tumor effects and may become viable treatments in the future.
Keywords: didesmethylrocaglamide; eIF4A inhibitors; natural compounds; neurofibromatosis (NF); protein translation; rocaglamide; signaling pathway; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Amaravathi, Oblinger, Welling, Kinghorn and Chang.
Conflict of interest statement
L-SC and AK: Patent: U.S. Provisional Application No. 19/55304 Anticancer rocaglamide derivatives. DW: Consultant: CereXis. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CTF meeting 2012: Translation of the basic understanding of the biology and genetics of NF1, NF2, and schwannomatosis toward the development of effective therapies.Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Mar;164A(3):563-78. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36312. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Am J Med Genet A. 2014. PMID: 24443315 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of MEK inhibitors in the treatment of plexiform neurofibromas.Childs Nerv Syst. 2020 Oct;36(10):2443-2452. doi: 10.1007/s00381-020-04731-2. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Childs Nerv Syst. 2020. PMID: 32607696 Review.
-
Current Understanding of Neurofibromatosis Type 1, 2, and Schwannomatosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 29;22(11):5850. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115850. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34072574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Available Therapies for Patients with Neurofibromatosis-Related Nervous System Tumors.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2020 Aug 7;21(10):81. doi: 10.1007/s11864-020-00779-z. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32767156 Review.
-
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and tumorigenesis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Neurosurg Focus. 2010 Jan;28(1):E8. doi: 10.3171/2009.11.FOCUS09221. Neurosurg Focus. 2010. PMID: 20043723
Cited by
-
A guide to ERK dynamics, part 2: downstream decoding.Biochem J. 2023 Dec 13;480(23):1909-1928. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20230277. Biochem J. 2023. PMID: 38038975 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic retroperitoneal resection of the duodenal gastrointestinal stromal tumors in neurofibromatosis type 1; Case Report and literature review.Front Surg. 2022 Aug 26;9:939705. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.939705. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36090331 Free PMC article.
-
Clinico-radiological features of optic nerve sheath schwannoma: Review and illustrative case.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar;35(2):456-465. doi: 10.1177/11206721241287575. Epub 2024 Sep 28. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39340435 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

