Exploration of Potential Diagnostic Value of Protein Content in Serum Small Extracellular Vesicles for Early-Stage Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma
- PMID: 34604046
- PMCID: PMC8479155
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.707658
Exploration of Potential Diagnostic Value of Protein Content in Serum Small Extracellular Vesicles for Early-Stage Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma
Abstract
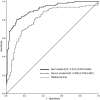
Epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC) is one of the most common gynecologic malignancies with a high mortality rate. Serum biomarkers and imaging approaches are insufficient in identifying EOC patients at an early stage. This study is to set up a combination of proteins from serum small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) for the diagnosis of early-stage EOC and to determine its performance. A biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer (BESOC) cohort was used as a Chinese multi-center population-based biomarker study and registered as a Chinese Clinical Trial ChiCTR2000040136. The sEV protein levels of CA125, HE4, and C5a were measured in 299 subjects. Logistic regression was exploited to calculate the odds ratio and to create the sEV protein model for the predicted probability and subsequently receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. The combined sEV marker panel of CA125, HE4, and C5a as a sEV model obtained an area under curve (AUC) of 0.912, which was greater than the serum model (0.809), by ROC analysis to identify EOC patients from the whole cohort. With the cutoff of 0.370, the sensitivity and specificity of the sEV model were 0.80 and 0.89, which were much better performance than the serum markers (sensitivity: 0.55~0.66; specificity: 0.59~0.68) and the risk of ovarian malignancy algorithm (ROMA) index approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (sensitivity: 0.65; specificity: 0.61), to identify EOC patients from patients with benign ovarian diseases or other controls. The sEV levels of CA125 significantly differed among early-stage and late-stage EOC (p < 0.001). Moreover, the AUC of ROC to identify early-stage EOC patients was 0.888. Further investigation revealed that the sEV levels of these 3 proteins significantly decreased after cytoreductive surgery (CA125, p = 0.008; HE4, p = 0.025; C5a, p = 0.044). In summary, our study showed that CA125, HE4, and C5a levels in serum sEVs can identify EOC patients at the early stage, elucidating the possibility of using a sEV model for the diagnosis of early-stage EOC.
Keywords: early diagnosis; epithelial ovarian carcinoma; multi-center population-based study; protein contents; serum; small extracellular vesicle.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Bai, Shan, Zhang, Liu, Zhu, Xu, Chen, Sheng, Deng, Guo, Zhang, Wang, Zhang and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors YB, ZL, XX, DZ, and YaZ were employed by 3D Medicines. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ROMA (Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm) for estimating the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer in women presenting with pelvic mass: is it really useful?Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011 Mar;49(3):521-5. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.075. Epub 2011 Feb 3. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011. PMID: 21288178
-
Diagnostic Model of Serum miR-193a-5p, HE4 and CA125 Improves the Diagnostic Efficacy of Epithelium Ovarian Cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2018 Oct;24(4):739-744. doi: 10.1007/s12253-018-0392-x. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Pathol Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 29520570
-
Modification of cut-off values for HE4, CA125 and the ROMA algorithm for early-stage epithelial ovarian cancer detection: Results from 1021 cases in South China.Clin Biochem. 2016 Jan;49(1-2):32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.07.029. Epub 2015 Aug 15. Clin Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26285075
-
The role of human epididymis protein 4 in the diagnosis of epithelial ovarian cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2016 Mar;18(3):233-9. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1365-0. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Clin Transl Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26220095 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Technology for Detecting Ovarian Cancer Biomarkers.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 27;15(23):5607. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235607. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067311 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of ovarian tumors: the emerging roles of CA125, HE4, and C5a.J Ovarian Res. 2024 Jan 5;17(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01336-6. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 38178252 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the extracellular vesicle network: insights into ovarian cancer metastasis and chemoresistance.Mol Cancer. 2024 Sep 16;23(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02103-x. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39285475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of label-free surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) of extracellular vesicles (EVs) with Raman tagged labels to enhance ovarian cancer diagnostics.Biosens Bioelectron. 2025 Nov 15;288:117800. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2025.117800. Epub 2025 Jul 18. Biosens Bioelectron. 2025. PMID: 40700940 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA) index in the detection of ovarian cancer in postmenopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Womens Health. 2025 Jun 5;25(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12905-025-03766-4. BMC Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40474158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robboy SJ, Russell P, Anderson MC, Prat J, Mutter GL. Robboy’s Pathology of the Female Reproductive Tract. New York, NY: Elsevier Health Sciences; (2009).
-
- Noone AM, Howlader N, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, et al. . (eds) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2015, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD: (2017) p. 25. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015/, based on November 2017 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous