Comparison of the Relative Diagnostic Performance of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18F]FDG PET/CT for the Detection of Bone Metastasis in Patients With Different Cancers
- PMID: 34604078
- PMCID: PMC8484883
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.737827
Comparison of the Relative Diagnostic Performance of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18F]FDG PET/CT for the Detection of Bone Metastasis in Patients With Different Cancers
Abstract
Purpose: The present retrospective analysis sought to compare the relative diagnostic efficacy of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 to that of [18F]FDG PET/CT as a means of detecting bone metastases in patients with a range of cancer types.
Materials: In total, 30 patients with bone metastases associated with different underlying malignancies were retrospectively enrolled. All patients had undergone [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18F]FDG PET/CT, and the McNemar test was used to compare the relative diagnostic performance of these two imaging modalities. The maximum standard uptake value (SUVmax) was used to quantify radiotracer uptake by metastatic lesions, with the relative uptake associated with these two imaging strategies being compared via the Mann-Whitney U test. The cohort was further respectively divided into two (osteolytic and osteoblastic bone metastases) and three clinical subgroups (lung cancer, thyroid cancer, and liver cancer).
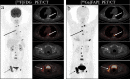
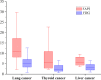
Results: [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT was found to be significantly more sensitive as a means of diagnosing bone metastases relative to [18F]FDG PET/CT ([109/109] 100% vs [89/109] 81.7%; P< 0.01), consistent with the significantly increased uptake of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 by these metastatic lesions relative to that of [18F]FDG (n=109, median SUVmax, 9.1 vs. 4.5; P< 0.01). [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 accumulation was significantly higher than that of [18F]FDG in both osteolytic (n=66, median SUVmax, 10.6 vs 6.1; P < 0.01), and osteoblastic metastases (n=43, median SUVmax, 7.7 vs 3.7; P < 0.01). [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 uptakes were significantly higher than that of [18F]FDG in bone metastases from lung cancer (n = 62, median SUVmax, 10.7 vs 5.2; P < 0.01), thyroid cancer (n = 18, median SUVmax, 5.65 vs 2.1; P < 0.01) and liver cancer (n = 12, median SUVmax, 5.65 vs 3.05; P < 0.01). However, [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 detected 10 false-positive lesions, while only 5 false-positive were visualized by [18F]FDG PET/CT.
Conclusion: [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT exhibits excellent diagnostic performance as a means of detecting bone metastases, and is superior to [18F]FDG PET/CT in this diagnostic context. Furthermore, [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 tracer uptake levels are higher than those of [18F]FDG for most bone metastases. However, owing to the potential for false-positive bone lesions, it is critical that physicians interpret all CT findings with caution to ensure diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: PET/CT; [18F]FDG; [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04; bone metastases; cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Wang, Liao, Rao, Gong, Ou, Chen and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A systematic review of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18F]FDG PET/CT in the diagnostic value of malignant tumor bone metastasis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 10;12:978506. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.978506. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36439440 Free PMC article.
-
Superiority of 68Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT to 18F-FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of different cancers with bone metastases.Bone. 2025 Jul;196:117426. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2025.117426. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Bone. 2025. PMID: 40086684
-
The potential utility of [68 Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 as a novel broad-spectrum oncological and non-oncological imaging agent-comparison with [18F]FDG.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Feb;49(3):963-979. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05522-w. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34410435
-
Comparison of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18F]FDG Uptake in Esophageal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 16;12:875081. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.875081. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35785188 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of FAPI PET imaging in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Theranostics. 2023 Aug 21;13(13):4694-4710. doi: 10.7150/thno.88335. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37649615 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Theranostics in targeting fibroblast activation protein bearing cells: Progress and challenges.Life Sci. 2023 Sep 15;329:121970. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121970. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37481033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of 68 Ga-FAPI PET/CT in patients with bone metastases in various cancers.Ann Nucl Med. 2024 Aug;38(8):630-638. doi: 10.1007/s12149-024-01935-3. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Ann Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 38684594
-
PET/CT with Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitors in Breast Cancer: Diagnostic and Theranostic Application-A Literature Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;15(3):908. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030908. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18F]FDG PET/CT in the diagnostic value of malignant tumor bone metastasis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 10;12:978506. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.978506. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36439440 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment and fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) PET: developments toward brain imaging.Front Nucl Med. 2023 Jul 18;3:1183471. doi: 10.3389/fnume.2023.1183471. eCollection 2023. Front Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 39355017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

