Benzopyrazine-Based Small Molecule Inhibitors As Trypanocidal and Leishmanicidal Agents: Green Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Silico Evaluations
- PMID: 34604170
- PMCID: PMC8484882
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.725892
Benzopyrazine-Based Small Molecule Inhibitors As Trypanocidal and Leishmanicidal Agents: Green Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Silico Evaluations
Abstract
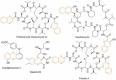
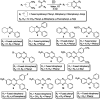
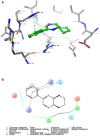
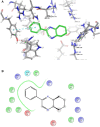
World Health Organization (WHO) identified twenty tropical disease categories as neglected tropical diseases (NTDs). Chagas' disease (also known as American trypanosomiasis) and leishmaniasis are two major classes of NTDs. The total number of mortality, morbidity, and disability attributed each year due to these two categories of diseases in magnitudes is much higher than the so-called elite diseases like cancer, diabetes, AIDS, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Impoverished communities around the world are the major victim of NTDs. The development of new and novel drugs in the battle against Chagas' disease and leishmaniasis is highly anticipated. An easy and straightforward on-water green access to synthesize benzopyrazines is reported. This ultrasound-assisted procedure does not require any catalyst/support/additive/hazardous solvents and maintains a high atom economy. A series of eleven benzopyrazines has been synthesized, and most of the synthesized compounds possess the drug-likeness following Lipinski's "Rule of 5". Benzopyrazines 3 and 4 demonstrated moderate leishmanicidal activity against L. mexicana (M378) strain. The selective lead compound 1 showed good leishmanicidal, and trypanocidal activities (in vitro) against both L. mexicana (M378) and T. cruzi (NINOA) strains compared to the standard controls. The in vitro trypanocidal and leishmanicidal activities of the lead compound 1 have been validated by molecular docking studies against four biomolecular drug targets viz. T. cruzi histidyl-tRNA synthetase, T. cruzi trans-sialidase, leishmanial rRNA A-site, and leishmania major N-myristoyl transferase.
Keywords: ecofriendly6; leishmanicidal2; on-water7; quinoxalines5; small molecule inhibitors4; trypanocidal1; trypanosoma cruzi3.
Copyright © 2021 Rock, Garcia, Espino, Shetu, Chan-Bacab, Moo-Puc, Patel, Rivera and Bandyopadhyay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Germacranolide-type sesquiterpene lactones from Smallanthus sonchifolius with promising activity against Leishmania mexicana and Trypanosoma cruzi.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Nov 13;10(1):567. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2509-6. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 29132413 Free PMC article.
-
Nifuroxazide and 4-Hydroxybenzhydrazone Derivatives as New Antiparasitic (Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania mexicana) and Anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis Agents.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 7;17(5):621. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050621. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40430911 Free PMC article.
-
A Practical Green Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Benzimidazoles Against Two Neglected Tropical Diseases: Chagas and Leishmaniasis.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(41):4714-4725. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666171201101807. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 23317160
-
Exploring microalgal and cyanobacterial metabolites with antiprotozoal activity against Leishmania and Trypanosoma parasites.Acta Trop. 2024 Mar;251:107116. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2023.107116. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Acta Trop. 2024. PMID: 38159713 Review.
-
Recent Theoretical Studies Concerning Important Tropical Infections.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(5):795-834. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190711121418. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31296154 Review.
Cited by
-
Small Molecule Therapeutics in the Pipeline Targeting for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Origin, Challenges, Opportunities, and Mechanisms of Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 6;25(11):6285. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116285. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892472 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Achutha L., Parameshwar R., Reddy B. M., Babu H. V. (2013). Microwave-assisted Synthesis of Some Quinoxaline-Incorporated Schiff Bases and Their Biological Evaluation. J. Chem. 2013, 578438. 10.1155/2013/578438 - DOI
-
- Bandyopadhyay D., Banik B. K. (2021). “Microwave-assisted Synthesis of Medicinally Privileged Heterocycles” in Advanced Synthetic Techniques, ed. Brahmachari G. Oxford, United Kingdom: Elsevier, 49–110.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

