Extracellular Vesicles in Reprogramming of the Ewing Sarcoma Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 34604225
- PMCID: PMC8484747
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.726205
Extracellular Vesicles in Reprogramming of the Ewing Sarcoma Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
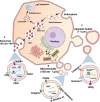
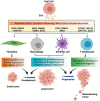
Ewing sarcoma (EwS) is a highly aggressive cancer and the second most common malignant bone tumor of children and young adults. Although patients with localized disease have a survival rate of approximately 75%, the prognosis for patients with metastatic disease remains dismal (<30%) and has not improved in decades. Standard-of-care treatments include local therapies such as surgery and radiotherapy, in addition to poly-agent adjuvant chemotherapy, and are often associated with long-term disability and reduced quality of life. Novel targeted therapeutic strategies that are more efficacious and less toxic are therefore desperately needed, particularly for metastatic disease, given that the presence of metastasis remains the most powerful predictor of poor outcome in EwS. Intercellular communication within the tumor microenvironment is emerging as a crucial mechanism for cancer cells to establish immunosuppressive and cancer-permissive environments, potentially leading to metastasis. Altering this communication within the tumor microenvironment, thereby preventing the transfer of oncogenic signals and molecules, represents a highly promising therapeutic strategy. To achieve this, extracellular vesicles (EVs) offer a candidate mechanism as they are actively released by tumor cells and enriched with proteins and RNAs. EVs are membrane-bound particles released by normal and tumor cells, that play pivotal roles in intercellular communication, including cross-talk between tumor, stromal fibroblast, and immune cells in the local tumor microenvironment and systemic circulation. EwS EVs, including the smaller exosomes and larger microvesicles, have the potential to reprogram a diversity of cells in the tumor microenvironment, by transferring various biomolecules in a cell-specific manner. Insights into the various biomolecules packed in EwS EVs as cargos and the molecular changes they trigger in recipient cells of the tumor microenvironment will shed light on various potential targets for therapeutic intervention in EwS. This review details EwS EVs composition, their potential role in metastasis and in the reprogramming of various cells of the tumor microenvironment, and the potential for clinical intervention.
Keywords: Ewing sarcoma; extracellular vesicles; immunosuppression; metastasis; reprogramming; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2021 Pachva, Lai, Jia, Rouleau and Sorensen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ewing Sarcoma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Impair Dendritic Cell Maturation and Function.Cells. 2021 Aug 13;10(8):2081. doi: 10.3390/cells10082081. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440851 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis.Cancer Cell. 2016 Dec 12;30(6):836-848. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.009. Cancer Cell. 2016. PMID: 27960084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current State of Immunotherapy and Mechanisms of Immune Evasion in Ewing Sarcoma and Osteosarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;15(1):272. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010272. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes from CD99-deprived Ewing sarcoma cells reverse tumor malignancy by inhibiting cell migration and promoting neural differentiation.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jun 17;10(7):471. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1675-1. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31209202 Free PMC article.
-
Suggested role for neutrophil extracellular trap formation in Ewing sarcoma immune microenvironment.Cancer Sci. 2024 Jan;115(1):36-47. doi: 10.1111/cas.15992. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 37915266 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Liquid biopsies in primary and secondary bone cancers.Cancer Drug Resist. 2022 Jun 21;5(3):541-559. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2022.17. eCollection 2022. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36176757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of small extracellular vesicle protein biomarkers for pediatric Ewing Sarcoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Apr 13;10:1138594. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1138594. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37122563 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating the nexus between gut-intratumoral microbiome and osteo-immune system in bone metastases.Bone Rep. 2024 Oct 10;23:101809. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2024.101809. eCollection 2024 Dec. Bone Rep. 2024. PMID: 39497943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD99 Modulates the Proteomic Landscape of Ewing Sarcoma Cells and Related Extracellular Vesicles.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 27;25(3):1588. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031588. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338867 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy in soft tissue and bone sarcoma: unraveling the barriers to effectiveness.Theranostics. 2022 Aug 15;12(14):6106-6129. doi: 10.7150/thno.72800. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36168619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

