IL-13 Alleviates Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis by Improving Fatty Acid Oxidation in Mitochondria
- PMID: 34604237
- PMCID: PMC8484794
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.736603
IL-13 Alleviates Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis by Improving Fatty Acid Oxidation in Mitochondria
Abstract
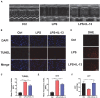
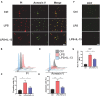
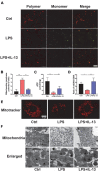
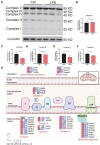
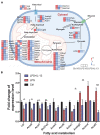
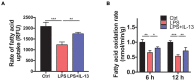
Sepsis-induced cardiac injury (SIC) is one of the most common complications in the intensive care unit (ICU) with high morbidity and mortality. Mitochondrial dysfunction is one of the main reasons for SIC, and Interleukin-13 (IL-13) is a master regulator of mitochondria biogenesis. The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of IL-13 in SIC and explore the underlying mechanism. It was found that reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and apoptosis were significantly increased in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated primary cardiomyocytes, which was accompanied with obvious mitochondria dysfunction. The results of RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq), mitochondrial membrane potential, fatty acid uptake and oxidation rate suggested that treatment with IL-13 could restore the function and morphology of mitochondria, indicating that it played an important role in protecting septic cardiomyocytes. These findings demonstrated that IL-13 alleviated sepsis-induced cardiac inflammation and apoptosis by improving mitochondrial fatty acid uptake and oxidation, suggesting that IL-13 may prove to be a potential promising target for SIC treatment.
Keywords: IL-13; cardiomyocyte apoptosis; fatty acid; mitochondria; sepsis.
Copyright © 2021 Guo, Hong, Zhang, Wei, Jin, Miao, Wang, Zhou, Wang and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Drosatos K., Drosatos-Tampakaki Z., Khan R., Homma S., Schulze P., Zannis V., et al. (2011). Inhibition of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase increases cardiac peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha expression and fatty acid oxidation and prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced heart dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 286 36331–36339. 10.1074/jbc.M111.272146 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

