miR-29b-3p Increases Radiosensitivity in Stemness Cancer Cells via Modulating Oncogenes Axis
- PMID: 34604239
- PMCID: PMC8481616
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.741074
miR-29b-3p Increases Radiosensitivity in Stemness Cancer Cells via Modulating Oncogenes Axis
Abstract
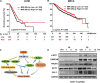
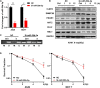
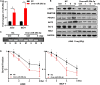
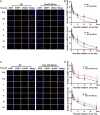
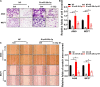
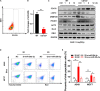
Radioresistance conferred by cancer stem cells (CSCs) is the principal cause of the failure of cancer radiotherapy. Eradication of CSCs is a prime therapeutic target and a requirement for effective radiotherapy. Three dimensional (3D) cell-cultured model could mimic the morphology of cells in vivo and induce CSC properties. Emerging evidence suggests that microRNAs (miRNAs) play crucial roles in the regulation of radiosensitivity in cancers. In this study, we aim to investigate the effects of miRNAs on the radiosensitivity of 3D cultured stem-like cells. Using miRNA microarray analysis in 2D and 3D cell culture models, we found that the expression of miR-29b-3p was downregulated in 3D cultured A549 and MCF7 cells compared with monolayer (2D) cells. Clinic data analysis from The Cancer Genome Atlas database exhibited that miR-29b-3p high expression showed significant advantages in lung adenocarcinoma and breast invasive carcinoma patients' prognosis. The subsequent experiments proved that miR-29b-3p overexpression decreased the radioresistance of cells in 3D culture and tumors in vivo through interfering kinetics process of DNA damage repair and inhibiting oncogenes RBL1, PIK3R1, AKT2, and Bcl-2. In addition, miR-29b-3p knockdown enhanced cancer cells invasion and migration capability. MiR-29b-3p overexpression decreased the stemness of 3D cultured cells. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that miR-29b-3p could be a sensitizer of radiation killing in CSC-like cells via inhibiting oncogenes expression. MiR-29b-3p could be a novel therapeutic candidate target for radiotherapy.
Keywords: miR-29b-3p; oncogene axis; radiosensitivity; stemness; three dimensional cultured cells.
Copyright © 2021 Pan, Du, Li, Shen, Liu, Li and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Asaithamby A., Hu B., Delgado O., Ding L. H., Story M. D., Minna J. D., et al. (2011). Irreparable complex DNA double-strand breaks induce chromosome breakage in organotypic three-dimensional human lung epithelial cell culture. Nucleic Acids Res. 39 5474–5488. 10.1093/nar/gkr149 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartel D. P. (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Berghauser Pont L. M. E., Spoor J. K. H., Venkatesan S., Swagemakers S., Kloezeman J. J., Dirven C. M., et al. (2014). The Bcl-2 inhibitor Obatoclax overcomes resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors SAHA and LBH589 as radiosensitizers in patient-derived glioblastoma stem-like cells. Genes Cancer 5 445–459. 10.18632/genesandcancer.42 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

