Breast Cancer-Related Neoplastic Alopecia: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 34604320
- PMCID: PMC8436715
- DOI: 10.1159/000514566
Breast Cancer-Related Neoplastic Alopecia: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
Neoplastic alopecia (NA) is defined as an organized hair loss in single or multiple areas of the scalp caused by a primary tumor that has metastasized to the skin of the scalp. Due to its localization and clinical appearance, NA should be placed in differential diagnosis with alopecia areata or other entities. To date, pathognomonic dermoscopic criteria of NA have not yet been described: the absence of classical criteria of other scalp diseases in addition to a major neovascularization with on-focus arborizing vessels and erosions or ulcerations may help the clinician to suspect a diagnosis of secondary alopecia. Dermatologists should pay more attention to these rare forms of secondarism because in exceptional cases, a simple alopecia of the scalp can hide a new, relapsing or metastatic neoplasia.
Keywords: Alopecia; Dermatopathology; Dermoscopy; Skin cancer.
Copyright © 2021 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare to have no conflicts of interest for the publication of this article.
Figures
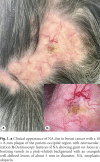

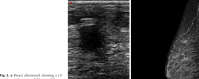
References
-
- De Giorgi V, Grazzini M, Alfaioli B, Savarese I, Corciova SA, Guerriero G, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of breast carcinoma. Dermatol Ther. 2010 Nov–Dec;23((6)):581–9. - PubMed
-
- Conforti C, Giuffrida R, Vezzoni R, Resende FSS, di Meo N, Zalaudek I. Dermoscopy and the experienced clinicians. Int J Dermatol. 2019 Jun 20 - PubMed
-
- Conforti C, Giuffrida R, Retrosi C, di Meo N, Zalaudek I. Two controversies confronting dermoscopy or dermatoscopy: nomenclature and results. Clin Dermatol. 2019 Sep–Oct;37((5)):597–9. - PubMed
-
- Cohen I, Levy E, Schreiber H. Alopecia neoplastica due to breast carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 1961;84((3)):490–2. - PubMed
-
- Dobson CM, Tagor V, Myint AS, Memon A. Telangiectatic metastatic breast carcinoma in face and scalp mimicking cutaneous angiosarcoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 Apr;48((4)):635–6. - PubMed

