Microscopic Detection of ASC Inflammasomes in Bone Marrow Derived Macrophages Post Stimulation
- PMID: 34604456
- PMCID: PMC8443463
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4151
Microscopic Detection of ASC Inflammasomes in Bone Marrow Derived Macrophages Post Stimulation
Abstract
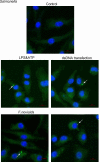
An inflammasome is an intracellular multiprotein complex that plays important roles in host defense and inflammatory responses. Inflammasomes are typically composed of the adaptor protein apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC), cytoplasmic sensor protein, and the effector protein pro-caspase-1. ASC assembly into a protein complex termed ASC speck is a readout for inflammasome activation. Here, we provide a step-by-step protocol for the detection of ASC speck by confocal microscopy in Bone marrow derived macrophages (BMBDs) triggered by chemical stimuli and bacterial pathogens. We also describe the detailed procedure for the generation of BMDMs, stimulating conditions for inflammasome activation, immunofluorescence cell staining of ASC protein, and microscopic examination. Thus far, this method is a simple and reliable manner to visualize and quantify the intracellular localization of ASC speck. Graphic abstract: Figure 1. Confocal microscopy detection of ASC speck formation in untreated WT BMDMs and WT BMDMs stimulated with LPS and ATP, transfected with dsDNA, and infected with F. novicida or Salmonella as indicated. Arrow indicates the ASC speck. Scale bars: 10 μm.
Keywords: AIM2; ASC; Confocal microscopy; Fluorescence staining; Inflammasome; NLRC4; NLRP3.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ASC speck formation as a readout for inflammasome activation.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1040:91-101. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-523-1_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23852599
-
Measuring NLR Oligomerization II: Detection of ASC Speck Formation by Confocal Microscopy and Immunofluorescence.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1417:145-58. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3566-6_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27221487
-
HUWE1 mediates inflammasome activation and promotes host defense against bacterial infection.J Clin Invest. 2020 Dec 1;130(12):6301-6316. doi: 10.1172/JCI138234. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 33104527 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mechanisms of inflammasome assembly.FEBS J. 2015 Feb;282(3):435-44. doi: 10.1111/febs.13133. Epub 2014 Nov 21. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25354325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances in formation and regulation of ASC-speck in inflammasome activation - A review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2016 Sep;56(9):1406-14. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 29738213 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Agrawal I. and Jha S.(2020). Comprehensive review of ASC structure and function in immune homeostasis and disease. Mol Biol Rep 47(4): 3077-3096. - PubMed
-
- Beilharz M., De Nardo D., Latz E. and Franklin B. S.(2016). Measuring NLR Oligomerization II: Detection of ASC Speck Formation by Confocal Microscopy and Immunofluorescence. Methods Mol Biol 1417: 145-158. - PubMed
-
- Hoss F., Rolfes V., Davanso M. R., Braga T. T. and Franklin B. S.(2018). Detection of ASC Speck Formation by Flow Cytometry and Chemical Cross-linking. Methods Mol Biol 1714: 149-165. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

