Molecular Dynamics Simulations Identify Tractable Lead-like Phenyl-Piperazine Scaffolds as eIF4A1 ATP-competitive Inhibitors
- PMID: 34604625
- PMCID: PMC8482399
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02805
Molecular Dynamics Simulations Identify Tractable Lead-like Phenyl-Piperazine Scaffolds as eIF4A1 ATP-competitive Inhibitors
Abstract
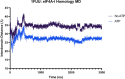
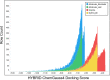
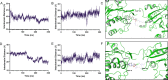
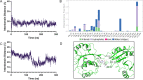
eIF4A1 is an ATP-dependent RNA helicase whose overexpression and activity have been tightly linked to oncogenesis in a number of malignancies. An understanding of the complex kinetics and conformational changes of this translational enzyme is necessary to map out all targetable binding sites and develop novel, chemically tractable inhibitors. We herein present a comprehensive quantitative analysis of eIF4A1 conformational changes using protein-ligand docking, homology modeling, and extended molecular dynamics simulations. Through this, we report the discovery of a novel, biochemically active phenyl-piperazine pharmacophore, which is predicted to target the ATP-binding site and may serve as the starting point for medicinal chemistry optimization efforts. This is the first such report of an ATP-competitive inhibitor for eiF4A1, which is predicted to bind in the nucleotide cleft. Our novel interdisciplinary pipeline serves as a framework for future drug discovery efforts for targeting eiF4A1 and other proteins with complex kinetics.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Chan K.; Robert F.; Oertlin C.; Kapeller-Libermann D.; Avizonis D.; Gutierrez J.; Handly-Santana A.; Doubrovin M.; Park J.; Schoepfer C.; Da Silva B.; Yao M.; Gorton F.; Shi J.; Thomas C. J.; Brown L. E.; Porco J. A. Jr.; Pollak M.; Larsson O.; Pelletier J.; Chio I. I. C. eIF4A supports an oncogenic translation program in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 515110.1038/s41467-019-13086-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Modelska A.; Turro E.; Russell R.; Beaton J.; Sbarrato T.; Spriggs K.; Miller J.; Graf S.; Provenzano E.; Blows F.; Pharoah P.; Caldas C.; Le Quesne J. The malignant phenotype in breast cancer is driven by eIF4A1-mediated changes in the translational landscape. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1603.10.1038/cddis.2014.542. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

