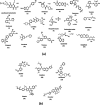
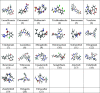
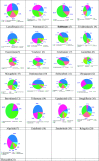
Theoretical Studies on the Molecular Properties, Toxicity, and Biological Efficacy of 21 New Chemical Entities
- PMID: 34604670
- PMCID: PMC8482469
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c03736
Theoretical Studies on the Molecular Properties, Toxicity, and Biological Efficacy of 21 New Chemical Entities
Abstract
New chemical entities (NCEs) such as small molecules and antibody-drug conjugates have strong binding affinity for biological targets, which provide deep insights into structure-specific interactions for the design of future drugs. As structures of drugs increase in complexity, the importance of computational predictions comes into sharp focus. Knowledge of various computational tools enables us to predict the molecular properties, toxicity, and biological efficacy of the drugs and help the medicinal chemists to discover new drugs more efficiently. Newly approved drugs have higher affinities for proteins and nucleic acids and are applied for the treatment of human diseases. We have carried out the computational studies of 21 such NCEs, specifically small molecules and antibody-drug conjugates, and studied the biological efficacy of these drugs. Their bioactivity score and molecular and pharmacokinetic properties were evaluated using online computer software programs, viz., Molinspiration and Osiris Property Explorer. The SwissTargetPrediction tool was used for the efficient prediction of protein targets for the NCEs. The results indicated higher stability for the drug complexes due to a larger HOMO-LUMO gap. A high electrophilicity index reflects good electrophilic behavior and high reactivity of the drugs. Lipinski's ''rule of five'' indicated that most of the drug complexes are likely to be orally active. These drugs also showed non-mutagenic, non-tumorigenic, non-irritant, and non-effective reproductive behavior. We hope that these studies will provide an insight into molecular recognition and definitely help the medicinal chemists to design new drugs in future.
© 2021 The Author. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computer-aided drug design and virtual screening of targeted combinatorial libraries of mixed-ligand transition metal complexes of 2-butanone thiosemicarbazone.Comput Biol Chem. 2018 Aug;75:178-195. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.05.008. Epub 2018 May 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29883916
-
Synthesis, molecular properties, toxicity and biological evaluation of some new substituted imidazolidine derivatives in search of potent anti-inflammatory agents.Saudi Pharm J. 2016 Jan;24(1):104-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Saudi Pharm J. 2016. PMID: 26903774 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Approaches to the New Drugs Approved During 2020.J Med Chem. 2022 Jul 28;65(14):9607-9661. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00710. Epub 2022 Jul 14. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35833579 Review.
-
Exploring the novel heterocyclic derivatives as lead molecules for design and development of potent anticancer agents.J Mol Graph Model. 2018 May;81:211-228. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2018.02.013. Epub 2018 Mar 9. J Mol Graph Model. 2018. PMID: 29609141
-
Synthetic Approaches to the New Drugs Approved During 2021.J Med Chem. 2023 Aug 10;66(15):10150-10201. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00501. Epub 2023 Aug 1. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37528515 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the 3,5-Dibromo-4,6-dimethoxychalcones and Their Flavone Derivatives as Dual α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibitors with Antioxidant and Anticancer Potential.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 17;13(10):1255. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101255. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456508 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Structural Derivatization of Flavonoid Acetamides Significantly Impacts Their Bioavailability and Antioxidant Properties.Molecules. 2022 Nov 22;27(23):8133. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238133. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500226 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Analysis of Bioactive Compounds from Leaves of Abrus precatorius L. (Rosary Pea) Against Breast Cancer.Cureus. 2024 Aug 26;16(8):e67808. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67808. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39323672 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of "magic chlorine" in drug discovery: an in silico approach.RSC Adv. 2023 Nov 30;13(49):34922-34934. doi: 10.1039/d3ra06638j. eCollection 2023 Nov 22. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38035236 Free PMC article.
-
Antiangiogenic potential of phytochemicals from Clerodendrum inerme (L.) Gaertn investigated through in silico and quantum computational methods.Mol Divers. 2025 Feb;29(1):215-239. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10846-4. Epub 2024 Apr 28. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 38678137
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous