Synthesis of 12β-Methyl-18- nor-bile Acids
- PMID: 34604682
- PMCID: PMC8482778
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04199
Synthesis of 12β-Methyl-18- nor-bile Acids
Abstract
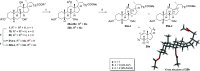
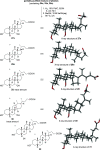
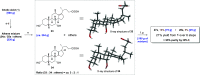
Decoupling the roles of the farnesoid X nuclear receptor and Takeda G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor 5 is essential for the development of novel bile acid therapeutics targeting metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. Herein, we describe the synthesis of 12β-methyl-18-nor-bile acids which may serve as probes in the search for new bile acid analogues with clinical applicability. A Nametkin-type rearrangement was applied to protected cholic acid derivatives, giving rise to tetra-substituted Δ13,14- and Δ13,17-unsaturated 12β-methyl-18-nor-bile acid intermediates (24a and 25a). Subsequent catalytic hydrogenation and deprotection yielded 12β-methyl-18-nor-chenodeoxycholic acid (27a) and its 17-epi-epimer (28a) as the two major reaction products. Optimization of the synthetic sequence enabled a chromatography-free route to prepare these bile acids at a multi-gram scale. In addition, the first cis-C-D ring-junctured bile acid and a new 14(13 → 12)-abeo-bile acid are described. Furthermore, deuteration experiments were performed to provide mechanistic insights into the formation of the formal anti-hydrogenation product 12β-methyl-18-nor-chenodeoxycholic acid (27a).
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Fiorucci S.; Distrutti E.. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology 256: Bile Acids and Their Receptors. 1st Ed.; Springer International Publishing, 2019. - PubMed
- Tazuma S.; Takikawa H.. Bile Acids in Gastroenterology: Basic and Clinical. 1st Ed.; Springer Japan, 2017.
- Jenkins G. J.; Hardie L. J.. Bile Acids: Toxicology and Bioactivity; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, 2008.
-
- Dawson P. A.; Karpen S. J. Intestinal transport and metabolism of bile acids. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1085–1099. 10.1194/jlr.r054114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Hofmann A. F. The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in mammals: form and functions. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 2584–2598. 10.2741/3399. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Makishima M.; Okamoto A. Y.; Repa J. J.; Tu H.; Learned R. M.; Luk A.; Hull M. V.; Lustig K. D.; Mangelsdorf D. J.; Shan B. Identification of a Nuclear Receptor for Bile Acids. Science 1999, 284, 1362–1365. 10.1126/science.284.5418.1362. - DOI - PubMed
- Parks D. J.; Blanchard S. G.; Bledsoe R. K.; Chandra G.; Consler T. G.; Kliewer S. A.; Stimmel J. B.; Willson T. M.; Zavacki A. M.; Moore D. D.; Lehmann J. M. Bile Acids: Natural Ligands for an Orphan Nuclear Receptor. Science 1999, 284, 1365–1368. 10.1126/science.284.5418.1365. - DOI - PubMed
- Wang H.; Chen J.; Hollister K.; Sowers L. C.; Forman B. M. Endogenous Bile Acids Are Ligands for the Nuclear Receptor FXR/BAR. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 543–553. 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80348-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

