Apocarotenals of Phenolic Carotenoids for Superior Antioxidant Activities
- PMID: 34604688
- PMCID: PMC8482777
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04432
Apocarotenals of Phenolic Carotenoids for Superior Antioxidant Activities
Abstract
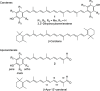
A series of para-phenolic carotenes 1 with ortho- and meta-substitutions were respectively prepared utilizing the benzenesulfonyl protection method, which demonstrated the importance of the ring substituents on their effective conjugation, evaluated by their UV absorption values. The corresponding apo-12'-carotenals 2 were devised to improve the conjugation effect of the para-phenolic radical with the polyene chain by the conjugated aldehyde group. Apo-12'-carotenals 2b and 2c without ortho-substituents exhibited superior antioxidant activities to their corresponding symmetrical carotenes 1 as well as β-carotene and apo-12'-β-carotenal in 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assays.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Oxo-Carotenoids as Efficient Superoxide Radical Scavengers.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 5;11(8):1525. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081525. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009244 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Antioxidant Activities and Polyphenol Contents of Seven Commercially Available Fruits.Pharmacognosy Res. 2016 Oct-Dec;8(4):258-264. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.188875. Pharmacognosy Res. 2016. PMID: 27695265 Free PMC article.
-
Spectroscopic studies on the antioxidant activity of p-coumaric acid.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2013 Nov;115:719-24. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.06.110. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2013. PMID: 23892112
-
Comparison of in vitro antioxidant and antiradical activities of L-tyrosine and L-Dopa.Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):431-8. doi: 10.1007/s00726-006-0379-x. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Amino Acids. 2007. PMID: 16932840
-
Characterization of the radical scavenging and antioxidant activities of danshensu and salvianolic acid B.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Jan;46(1):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.06.034. Epub 2007 Jul 4. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 17719161
Cited by
-
Oxo-Carotenoids as Efficient Superoxide Radical Scavengers.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 5;11(8):1525. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081525. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009244 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodotorula mucilaginosa-alternative sources of natural carotenoids, lipids, and enzymes for industrial use.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 14;8(11):e11505. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11505. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36419653 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Polívka T.; Sundström V. Ultrafast Dynamics of Carotenoid Excited States–From Solution to Natural and Artificial Systems. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2021–2071. 10.1021/cr020674n. - DOI - PubMed
- Holt N. E.; Zigmantas D.; Valkunas L.; Li X.-P.; Niyogi K. K.; Fleming G. R. Carotenoid Cation Formation and the Regulation of Photosynthetic Light Harvesting. Science 2005, 307, 433–436. 10.1126/science.1105833. - DOI - PubMed
- Wormit M.; Harbach P. H. P.; Mewes J. M.; Amarie S.; Wachtveitl J.; Dreuw A. Excitation energy transfer and carotenoid radical cation formation in light harvesting complexes – A theoretical perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Bioenerg. 2009, 1787, 738–746. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.01.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krinsky N. I.; Yeum K.-J. Carotenoid–radical interactions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 305, 754–760. 10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00816-7. - DOI - PubMed
- El-Agamey A.; Lowe G. M.; McGarvey D. J.; Mortensen A.; Phillip D. M.; Truscott T. G.; Young A. J. Carotenoid radical chemistry and antioxidant/pro-oxidant properties. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 430, 37–48. 10.1016/j.abb.2004.03.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burton G. W.; Ingold K. U. β-Carotene: An Unusual Type of Lipid Antioxidant. Science 1984, 224, 569–573. 10.1126/science.6710156. - DOI - PubMed
- Terao J. Antioxidant Activity of β-Carotene-Related Carotenoids in Solution. Lipids 1989, 24, 659–661. 10.1007/BF02535085. - DOI - PubMed
- Stahl W.; Sies H. Antioxidant activity of carotenoids. Mol. Aspects Med. 2003, 24, 345–351. 10.1016/S0098-2997(03)00030-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

