New Ultra-minimally Invasive Surgical Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Analysis of Comparative Outcomes
- PMID: 34604814
- PMCID: PMC8473553
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euros.2021.08.009
New Ultra-minimally Invasive Surgical Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Analysis of Comparative Outcomes
Abstract
Context: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) associated with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) is diagnosed in up to 80% of men during their lifetime. Several novel ultra-minimally invasive surgical treatments (uMISTs) for BPH/benign prostatic obstruction (BPO) have become available over the past 5 yr.
Objective: To evaluate the perioperative and functional outcomes of recently introduced uMISTs for BPH/BPO, including Urolift, Rezūm, temporary implantable nitinol device, prostatic artery embolization (PAE), and intraprostatic injection.
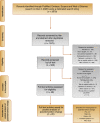
Evidence acquisition: A systematic literature search was conducted in December 2020 using Medline (via PubMed), Embase (via Ovid), Scopus, and Web of Science (registered on PROSPERO as CRD42021225014). The search strategy used PICO criteria and article selection was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. The risk of bias and the quality of the articles included were assessed. A dedicated data extraction form was used to collect the data of interest. Pooled and cumulative analyses were performed to compare perioperative and functional outcomes between study groups. A random-effects model using the DerSimonian and Laird method was used to evaluate heterogeneity. Stata version 15.0 software was used for all statistical analyses.
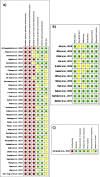
Evidence synthesis: The initial electronic search identified 3978 papers, of which 48 ultimately met the inclusion criteria and were included in the analysis. Pooled analysis revealed a uMIST benefit in terms of International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS; -9.81 points, 95% confidence interval [CI] -11.37 to -8.25 at 1 mo; -13.13 points, 95% CI -14.98 to -11.64 at 12 mo), maximum flow rate (from +3.66 ml/s, 95% CI 2.8-4.5 to +4.14 ml/s, 95% CI 0.72-7.56 at 12 mo), and postvoid residual volume (-10.10 ml, 95% CI -27.90 to 7.71 at 12 mo). No negative impact was observed on scores for the International Index of Erectile Function-5, Male Sexual Health Questionnaire-Ejaculatory Dysfunction bother and function scales (overall postintervention change in pooled median score of 1.88, 95% CI 1.34-2.42 at the start of follow-up; and 1.04, 95% CI 0.28-1.8 after 1 yr), or the IPSS-Quality of Life questionnaire.
Conclusions: Novel uMISTs can yield fast and effective relief of LUTS without affecting patient quality of life. Only Rezūm, UroLift, and PAE had a minimal impact on patients' sexual function with respect to baseline, especially regarding preservation of ejaculation.
Patient summary: We reviewed outcomes for recently introduced ultra-minimally invasive surgical treatments for patients with lower urinary tract symptoms caused by benign prostate enlargement or obstruction. The evidence suggests that these novel techniques are beneficial in terms of controlling symptoms while preserving sexual function.
Take home message: Novel ultra-minimally invasive treatments can yield fast and effective relief of lower urinary tract symptoms without affecting a patient's quality of life.
Keywords: Benign prostatic hyperplasia; Ejaculation; Lower urinary tract symptoms; Micturition; Ultra-minimally invasive.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Emerging Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms.Eur Urol. 2017 Dec;72(6):986-997. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.07.005. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28734706 Review.
-
Aquablation of the prostate for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 13;2(2):CD013143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013143.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30759311 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Prostate Artery Embolization on Different Qualities of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Obstruction.Eur Urol Focus. 2022 Sep;8(5):1323-1330. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2022.01.011. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Eur Urol Focus. 2022. PMID: 35125344
-
Prostatic urethral lift (UroLift) versus convective water vapor ablation (Rezum) for minimally invasive treatment of BPH: a comparison of improvements and durability in 3-year clinical outcomes.Can J Urol. 2021 Oct;28(5):10824-10833. Can J Urol. 2021. PMID: 34657655 Clinical Trial.
-
Complication rate across the minimally invasive surgical treatments (MISTs): where do we stand? A systematic review of the literature.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2024 Oct 22. doi: 10.1038/s41391-024-00900-5. Online ahead of print. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2024. PMID: 39438691 Review.
Cited by
-
Intermediate-term oncological and functional outcomes in prostate cancer patients treated with perineal robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: A single center analysis.Asian J Urol. 2023 Oct;10(4):423-430. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2023.05.005. Epub 2023 Aug 19. Asian J Urol. 2023. PMID: 38024441 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging-guided transurethral ultrasound ablation for benign prostatic obstruction: 1-year clinical outcomes of a phase II study.BJU Int. 2025 Sep;136(3):473-483. doi: 10.1111/bju.16795. Epub 2025 May 28. BJU Int. 2025. PMID: 40432395 Free PMC article.
-
Transperineal laser ablation as a new minimally invasive surgical therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review of existing literature.Ther Adv Urol. 2023 Sep 21;15:17562872231198634. doi: 10.1177/17562872231198634. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Urol. 2023. PMID: 37745187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting Early Outcomes of Prostatic Artery Embolization Using n-Butyl Cyanoacrylate Liquid Embolic Agent: A Machine Learning Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 28;15(11):1351. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15111351. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40506923 Free PMC article.
-
Composite urinary and sexual outcomes after Rezum: an analysis of predictive factors from an Italian multi-centric study.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023 Jun;26(2):410-414. doi: 10.1038/s41391-022-00587-6. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023. PMID: 36042295
References
-
- Sun Y., Peng B., Lei G.L., Wei Q., Yang L. Study of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors and α-adrenoceptor antagonists used alone or in combination for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2020;72:13–21. doi: 10.23736/S0393-2249.19.03408-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Capogrosso P., Fallara G., Pozzi E., Schifano N., Candela L., Costa A., Boeri L., Belladelli F., Cazzaniga W., Scattoni V., Salonia A., Montorsi F. Rates and predictors of postoperative complications after Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) at a high-volume center. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2021 doi: 10.23736/S2724-6051.21.04315-9. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33887894. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

