Intradermal-delivered DNA vaccine induces durable immunity mediating a reduction in viral load in a rhesus macaque SARS-CoV-2 challenge model
- PMID: 34604818
- PMCID: PMC8479327
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100420
Intradermal-delivered DNA vaccine induces durable immunity mediating a reduction in viral load in a rhesus macaque SARS-CoV-2 challenge model
Abstract
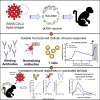
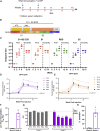
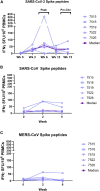
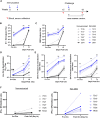
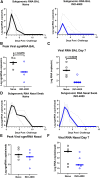
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has had a dramatic global impact on public health and social and economic infrastructures. Here, we assess the immunogenicity and anamnestic protective efficacy in rhesus macaques of an intradermal (i.d.)-delivered SARS-CoV-2 spike DNA vaccine, INO-4800, currently being evaluated in clinical trials. Vaccination with INO-4800 induced T cell responses and induced spike antigen and RBD binding antibodies with ADCP and ADCD activity. Sera from the animals neutralized both the D614 and G614 SARS-CoV-2 pseudotype viruses. Several months after vaccination, animals were challenged with SARS-CoV-2 resulting in rapid recall of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein T cell and neutralizing antibody responses. These responses were associated with lower viral loads in the lung. These studies support the immune impact of INO-4800 for inducing both humoral and cellular arms of the adaptive immune system, which are likely important for providing durable protection against COVID-19 disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; ID DNA vaccine; SARS-CoV-2; challenge; coronavirus; electroporation; infectious disease; macaque; protection.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.P., E.L.R., E.P., E.N.G., M.P., S.N.W., P.B., Z.X., S.M.R., K.Y.K., N.C., E.T-R., J.C., N.J.T., K.M., and D.K.W. declare no competing interests. J.N.W., K.S., I.M., Z.E., D.G., A.D., D.E., A.G., V.M.A., J.J.K., L.M.H., S.J.R., T.R.F.S., and K.E.B. are employees of Inovio Pharmaceuticals and as such receive salary and benefits, including ownership of stock and stock options, from the company. D.B.W. discloses the following paid associations with commercial partners: GeneOne (Consultant), Geneos (Advisory Board), Astrazeneca (Advisory Board, Speaker), Inovio (BOD, SRA, Stock), Pfizer (Speaker), Merck (Speaker), Sanofi (Advisory Board), BBI (Advisory Board).
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques.Science. 2020 Aug 14;369(6505):806-811. doi: 10.1126/science.abc6284. Epub 2020 May 20. Science. 2020. PMID: 32434945 Free PMC article.
-
A human cell-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine elicits potent neutralizing antibody responses and protects mice from SARS-CoV-2 challenge.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):1555-1573. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1957400. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 34304724 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses Induced by Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccines in a Real-World Setting.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:802858. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.802858. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003131 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 induced by infection or vaccination.J Intern Med. 2022 Jan;291(1):32-50. doi: 10.1111/joim.13372. Epub 2021 Aug 5. J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 34352148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accelerating model-informed decisions for COVID-19 vaccine candidates using a model-based meta-analysis approach.EBioMedicine. 2022 Oct;84:104264. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104264. Epub 2022 Sep 28. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 36182824 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
LAMP1 targeting of the large T antigen of Merkel cell polyomavirus results in potent CD4 T cell responses and tumor inhibition.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 30;14:1253568. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1253568. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37711623 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Trimeric Spike Protein Associated to Poly(I:C) Plus Alum.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 30;13:884760. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.884760. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844561 Free PMC article.
-
Status Report on COVID-19 Vaccines Development.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2021;23(6):9. doi: 10.1007/s11908-021-00752-3. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2021. PMID: 33867863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of a highly thermotolerant, immunogenic SARS-CoV-2 spike fragment.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100025. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.016284. Epub 2020 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33154165 Free PMC article.
-
Classical and Next-Generation Vaccine Platforms to SARS-CoV-2: Biotechnological Strategies and Genomic Variants.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 18;19(4):2392. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19042392. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35206580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thanh Le T., Andreadakis Z., Kumar A., Gómez Román R., Tollefsen S., Saville M., Mayhew S. The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020;19:305–306. - PubMed
-
- FDA . US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration; 2020. COVID-19 Vaccines.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

