The primary visual cortex of Cetartiodactyls: organization, cytoarchitectonics and comparison with perissodactyls and primates
- PMID: 34604923
- PMCID: PMC9046356
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-021-02392-8
The primary visual cortex of Cetartiodactyls: organization, cytoarchitectonics and comparison with perissodactyls and primates
Abstract
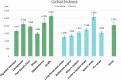
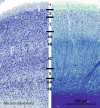
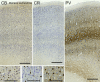
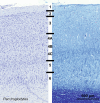
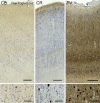
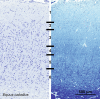
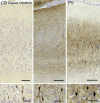
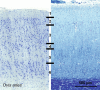
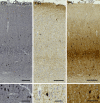
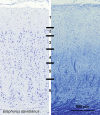
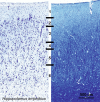
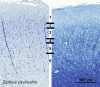
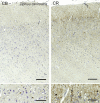
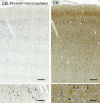
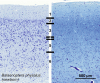
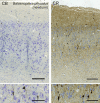
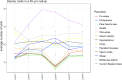
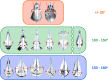
Cetartiodactyls include terrestrial and marine species, all generally endowed with a comparatively lateral position of their eyes and a relatively limited binocular field of vision. To this day, our understanding of the visual system in mammals beyond the few studied animal models remains limited. In the present study, we examined the primary visual cortex of Cetartiodactyls that live on land (sheep, Père David deer, giraffe); in the sea (bottlenose dolphin, Risso's dolphin, long-finned pilot whale, Cuvier's beaked whale, sperm whale and fin whale); or in an amphibious environment (hippopotamus). We also sampled and studied the visual cortex of the horse (a closely related perissodactyl) and two primates (chimpanzee and pig-tailed macaque) for comparison. Our histochemical and immunohistochemical results indicate that the visual cortex of Cetartiodactyls is characterized by a peculiar organization, structure, and complexity of the cortical column. We noted a general lesser lamination compared to simians, with diminished density, and an apparent simplification of the intra- and extra-columnar connections. The presence and distribution of calcium-binding proteins indicated a notable absence of parvalbumin in water species and a strong reduction of layer 4, usually enlarged in the striated cortex, seemingly replaced by a more diffuse distribution in neighboring layers. Consequently, thalamo-cortical inputs are apparently directed to the higher layers of the column. Computer analyses and statistical evaluation of the data confirmed the results and indicated a substantial correlation between eye placement and cortical structure, with a markedly segregated pattern in cetaceans compared to other mammals. Furthermore, cetacean species showed several types of cortical lamination which may reflect differences in function, possibly related to depth of foraging and consequent progressive disappearance of light, and increased importance of echolocation.
Keywords: Cetartiodactyls; Comparative neuroanatomy; Cytoarchitecture; Lamination; Lateralization; Visual cortex.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures














Similar articles
-
The neocortex of cetartiodactyls. II. Neuronal morphology of the visual and motor cortices in the giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis).Brain Struct Funct. 2015 Sep;220(5):2851-72. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0830-9. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Brain Struct Funct. 2015. PMID: 25048683
-
Marine Mammals in the Mediterranean Sea: An Overview.Adv Mar Biol. 2016;75:1-36. doi: 10.1016/bs.amb.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Adv Mar Biol. 2016. PMID: 27770981
-
Interspecies Retinal Diversity and Optic Nerve Anatomy in Odontocetes.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 6;13(21):3430. doi: 10.3390/ani13213430. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958185 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical complexity in cetacean brains.Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2005 Nov;287(1):1142-52. doi: 10.1002/ar.a.20258. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16200644 Review.
-
[Viruses of whales and dolphins].Mikrobiol Z. 1996 Sep-Oct;58(5):100-6. Mikrobiol Z. 1996. PMID: 9044706 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
A brief sketch across multiscale and comparative neuroanatomical features.Front Neuroanat. 2023 Feb 13;17:1108363. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2023.1108363. eCollection 2023. Front Neuroanat. 2023. PMID: 36861111 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mapping sheep to human brain: The need for a sheep brain atlas.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jul 29;9:961413. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.961413. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35967997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroanatomy of the Cetacean Sensory Systems.Animals (Basel). 2023 Dec 23;14(1):66. doi: 10.3390/ani14010066. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38200796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The orbitofrontal cortex of the sheep. Topography, organization, neurochemistry, digital tensor imaging and comparison with the chimpanzee and human.Brain Struct Funct. 2022 Jun;227(5):1871-1891. doi: 10.1007/s00429-022-02479-w. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Brain Struct Funct. 2022. PMID: 35347401 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing advances in the future of primate neuroscience research.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2022 Dec 13;4:100064. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2022.100064. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36582401 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allman J, McGuinness E. Visual cortex in primates. Comp Primate Biol. 1988;4:279–326.
-
- Arboretti R, Bonnini S, Corain L, Salmaso L. A permutation approach for ranking of multivariate populations. J Multivar Anal. 2014;132:39–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jmva.2014.07.009. - DOI
-
- Bailey P, von Bonin G, McCulloch WS. The isocortex of the chimpanzee. University of Illinois Press; 1950.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

