Efficacy of mirabegron, a β3 -adrenoreceptor agonist, in Japanese women with overactive bladder and either urgency urinary incontinence or mixed urinary incontinence: Post-hoc analysis of pooled data from two randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies
- PMID: 34605079
- PMCID: PMC9293404
- DOI: 10.1111/iju.14700
Efficacy of mirabegron, a β3 -adrenoreceptor agonist, in Japanese women with overactive bladder and either urgency urinary incontinence or mixed urinary incontinence: Post-hoc analysis of pooled data from two randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies
Abstract
Objective: To confirm if mirabegron 50 mg shows efficacy in women with overactive bladder and either urgency urinary incontinence or mixed urinary incontinence versus placebo.
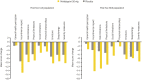
Methods: Post-hoc analyses were carried out using pooled data from a Japanese phase IIb and a phase III study. The primary efficacy end-point was baseline to end-of-treatment change in the mean number of micturitions/24 h. The secondary end-points were changes in the mean voided volume/micturition, mean number of urgency and incontinence episodes/24 h, and mean number of nocturia episodes/night. Other end-points were quality of life and incontinence normalization rates.
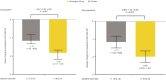
Results: Women with urgency urinary incontinence (placebo n = 204, mirabegron n = 214) and mixed urinary incontinence (placebo n = 122, mirabegron n = 139) were included. Change in mean micturitions/24 h at end-of-treatment for mirabegron was statistically significant versus placebo in both populations; the effect size increased over time. For all secondary end-points, median changes for mirabegron were statistically significant versus placebo at end-of-treatment, except for nocturia for the urgency urinary incontinence population and urgency for the mixed urinary incontinence population. Mirabegron showed larger improvements versus placebo in all quality-of-life domains, except for general health perception in the urgency urinary incontinence population. Incontinence normalization rates for mirabegron were 47.2% and 49.6% in the urgency urinary incontinence and mixed urinary incontinence populations, respectively, versus 42.6% and 39.3% for placebo.
Conclusions: Mirabegron 50 mg significantly improved key overactive bladder symptoms versus placebo in women with urgency urinary incontinence, and it also improved most overactive bladder symptoms, including micturition frequency, in patients with mixed urinary incontinence. These findings support the benefits of using mirabegron in the female overactive bladder wet population.
Keywords: mirabegron; overactive bladder; urinary incontinence; β3-adrenoreceptor agonist.
© 2021 Astellas Pharma Inc. International Journal of Urology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of the Japanese Urological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Satoru Takahashi is a consultant for Astellas. Yuji Mishima, Kentaro Kuroishi and Masashi Ukai are employees of Astellas Pharma.
Figures
Comment in
-
Editorial Comment to Efficacy of mirabegron, a β3 -adrenoreceptor agonist, in Japanese women with overactive bladder and either urgency urinary incontinence or mixed urinary incontinence: Post-hoc analysis of pooled data from two randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies.Int J Urol. 2022 Jan;29(1):15-16. doi: 10.1111/iju.14716. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Int J Urol. 2022. PMID: 34605071 No abstract available.
References
-
- Coyne KS, Sexton CC, Irwin DE, Kopp ZS, Kelleher CJ, Milsom I. The impact of overactive bladder, incontinence and other lower urinary tract symptoms on quality of life, work productivity, sexuality and emotional well‐being in men and women: results from the EPIC study. BJU Int. 2008; 101: 1388–95. - PubMed
-
- Irwin DE, Milsom I, Kopp Z, Abrams P, Cardozo L. Impact of overactive bladder symptoms on employment, social interactions and emotional well‐being in six European countries. BJU Int. 2006; 97: 96–100. - PubMed
-
- Papanicolaou S, Hunskaar S, Lose G, Sykes D. Assessment of bothersomeness and impact on quality of life of urinary incontinence in women in France, Germany, Spain and the UK. BJU Int. 2005; 96: 831–8. - PubMed
-
- Milsom I, Kaplan SA, Coyne KS, Sexton CC, Kopp ZS. Effect of bothersome overactive bladder symptoms on health‐related quality of life, anxiety, depression, and treatment seeking in the United States: results from EpiLUTS. Urology 2012; 80: 90–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

