Rapid high-resolution melting method to identify human leukocyte antigen-G (HLA-G) 3' untranslated region polymorphism +3142C/G (rs1063320)
- PMID: 34605219
- PMCID: PMC8606219
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.1817
Rapid high-resolution melting method to identify human leukocyte antigen-G (HLA-G) 3' untranslated region polymorphism +3142C/G (rs1063320)
Abstract
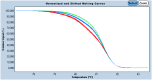
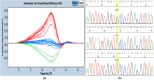
Background: HLA-G is a non-classical class I gene of the human Major Histocompatibility encoding molecules with immune-modulatory properties. Expression of HLA-G is being largely studied in pathological conditions, such as tumors, viral infections, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases, grafted tissues, among others. HLA-G +3142C/G (rs1063320: dbSNP database) polymorphism is located in 3' UTR of HAL-G and plays a key role in determining the magnitude of gene and protein expression. The detection of HLA-G +3142C/G polymorphism in the most published report is done through polymerase chain reaction followed by enzymatic digestion. Therefore, it is so interesting to develop a rapid and sensitive assay to genotype HLA-G +3142C/G polymorphism. High-resolution melt analysis (HRM) is a technology that is based on the analysis of the melting profile of PCR products through gradual temperature increase. The aim of this work is to apply high-resolution melt method for genotyping the HLA-G +3142C/G polymorphism.
Methods: DNA from 118 individuals was extracted from whole blood with QIAamp® DNA blood mini kit (Qiagen, Germany). Primer couple was designed using Primer 3 online tools so as to have only one SNP in the target sequence for high HRM efficiency. Positive Controls were identified using DNA sequencing and used as reference when assigning genotypes for trial samples.
Results: We were able to recognize the three genotypes with similar accuracy than DNA sequencing using high resolution melting method. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium test shows that our population is in equilibrium for the studied SNP. Genotypes frequencies of +3142C/G polymorphism in Tunisian general population are 0.475 for heterozygote G/C, 0.186 for homozygote G/G and 0.339 for homozygote C/C.
Conclusion: HRM is a cost-effective method suitable for SNP genotyping.
© 2021 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ben Fredj, N. et al (2016). The association between functional HLA‐G 14bp insertion/deletion and +3142 C>G polymorphisms and susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. Immunology Letters, 180, 24–30. - PubMed
-
- Bortolotti, D. et al (2012). An accurate and reliable real time SNP genotyping assay for the HLA‐G +3142 bp C>G polymorphism. Tissue Antigens, 80(3), 259–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

