Correlation of dual energy computed tomography electron density measurements with cerebral glioma grade
- PMID: 34605334
- PMCID: PMC9244748
- DOI: 10.1177/19714009211047455
Correlation of dual energy computed tomography electron density measurements with cerebral glioma grade
Abstract
Objective: To correlate dual energy computed tomography electron density measurements with histopathological cerebral glioma grading to determine whether it can be used as a non-invasive predictor of cerebral glioma grade.
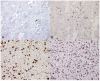
Materials and methods: Fifty patients with suspected cerebral gliomas on imaging scheduled to undergo resection were included. We tested our hypothesis that with increasing glioma grade, increased tumor cellularity should translate into increased electron density and if a statistically significant difference between electron density of low-grade gliomas and high-grade gliomas is seen, we may have a clinical use of dual energy computed tomography as a non-invasive tool to predict cerebral glioma grade.A pre-operative dual energy computed tomography scan of the brain was performed, and electron density measurements calculated from the solid part of the tumor. Obtaining a ratio with electron density of contralateral normal brain parenchyma normalized these values. The minimum, maximum and mean electron density and their normalized values recorded between high-grade gliomas and low-grade gliomas were compared for presence of statistical significance.
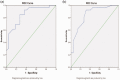
Results: A statistically significant difference was found between all six parameters recorded (minimum electron density and normalized values, mean electron density and normalized values, maximum electron density and normalized values) between low-grade gliomas and high-grade gliomas. The predictivity ranged from 75% (for minimum electron density and maximum normalized values) to 81.25% (for mean normalized values). All six parameters were found to have statistically significant positive correlation with Ki-67 index.
Conclusion: Dual energy computed tomography electron density measurements in cerebral gliomas are predictive of pre-operative differentiation of low-grade gliomas from high-grade gliomas and show a linear, statistically significant positive correlation with Ki-67 index.
Keywords: Dual energy computed tomography; cerebral glioma; electron density.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Osborn AG. Osborn’s Brain: Imaging, pathology and anatomy. Salt Lake City: Amirsys Inc; 2013. p.445.
-
- Law M, Cha S, Knopp EA, et al. High-grade gliomas and solitary metastases: Differentiation by using perfusion and proton spectroscopic MR imaging. Radiology 2002; 222: 715–21. - PubMed
-
- Teng K, Zhang ZH, Jiang LL. The application of apparent diffusion coefficient in preoperative grading of gliomas. J Med Imaging 2007; 17: 1250–51.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

