Using photocaging for fast time-resolved structural biology studies
- PMID: 34605426
- PMCID: PMC8489231
- DOI: 10.1107/S2059798321008809
Using photocaging for fast time-resolved structural biology studies
Abstract
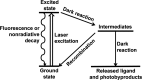
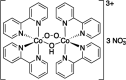
Careful selection of photocaging approaches is critical to achieve fast and well synchronized reaction initiation and perform successful time-resolved structural biology experiments. This review summarizes the best characterized and most relevant photocaging groups previously described in the literature. It also provides a walkthrough of the essential factors to consider in designing a suitable photocaged molecule to address specific biological questions, focusing on photocaging groups with well characterized spectroscopic properties. The relationships between decay rates (k in s-1), quantum yields (ϕ) and molar extinction coefficients (ϵmax in M-1 cm-1) are highlighted for different groups. The effects of the nature of the photocaged group on these properties is also discussed. Four main photocaging scaffolds are presented in detail, o-nitrobenzyls, p-hydroxyphenyls, coumarinyls and nitrodibenzofuranyls, along with three examples of the use of this technology. Furthermore, a subset of specialty photocages are highlighted: photoacids, molecular photoswitches and metal-containing photocages. These extend the range of photocaging approaches by, for example, controlling pH or generating conformationally locked molecules.
Keywords: photocages; reaction initiation; serial crystallography; time-resolved structural biology.
open access.
Figures




References
-
- Aarhus, R., Gee, K. & Lee, H. C. (1995). J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7745–7749. - PubMed
-
- Asido, M., Eberhardt, P., Kriebel, C. N., Braun, M., Glaubitz, C. & Wachtveitl, J. (2019). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 4461–4471. - PubMed
-
- Aujard, I., Benbrahim, C., Gouget, M., Ruel, O., Baudin, J., Neveu, P. & Jullien, L. (2006). Chem. Eur. J. 12, 6865–6879. - PubMed
-
- Barth, A., Corrie, J. E. T., Gradwell, M. J., Maeda, Y., Mäntele, W., Meier, T. & Trentham, D. R. (1997). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 4149–4159.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

